Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT ENGLISH-TRIANGLES-EXERCISE 7.1
- AD and BC are equal perpendiculars to a line segment AB (see Fig. 7.1...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a quadrilateral in which and/D A B\ =/C B A(see Fig. 7.17). P...
Text Solution
|
- In quadrilateral ACBD, A C\ =\ A Dand AB bisects /A(see Fig. 7.16). S...
Text Solution
|
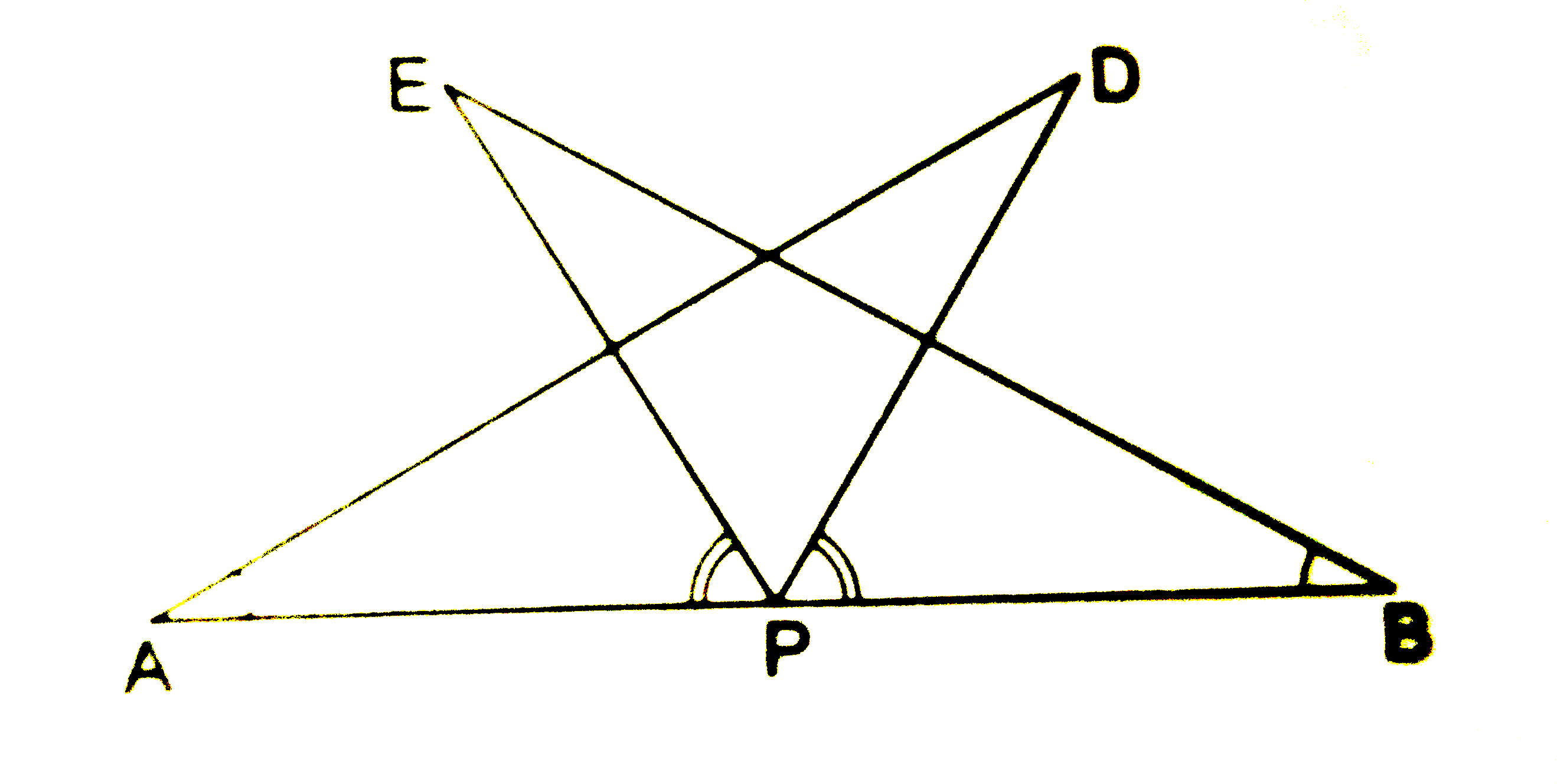
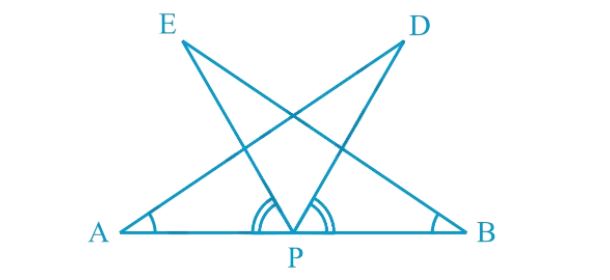
- AB is a line segment and P is its midpoint. D and E are points on the ...
Text Solution
|
- In right triangle ABC, right-angled at C, M is the mid-point of hypote...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure, A C=A E ,\ A B=A D\ a n d\ /B A D=/E A Cdot Prove that B C=...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure, line l is the bisector of angle A\ a n d\ B is any point...
Text Solution
|
- l\ a n d\ m are two parallel lines intersected by another pair of p...
Text Solution
|