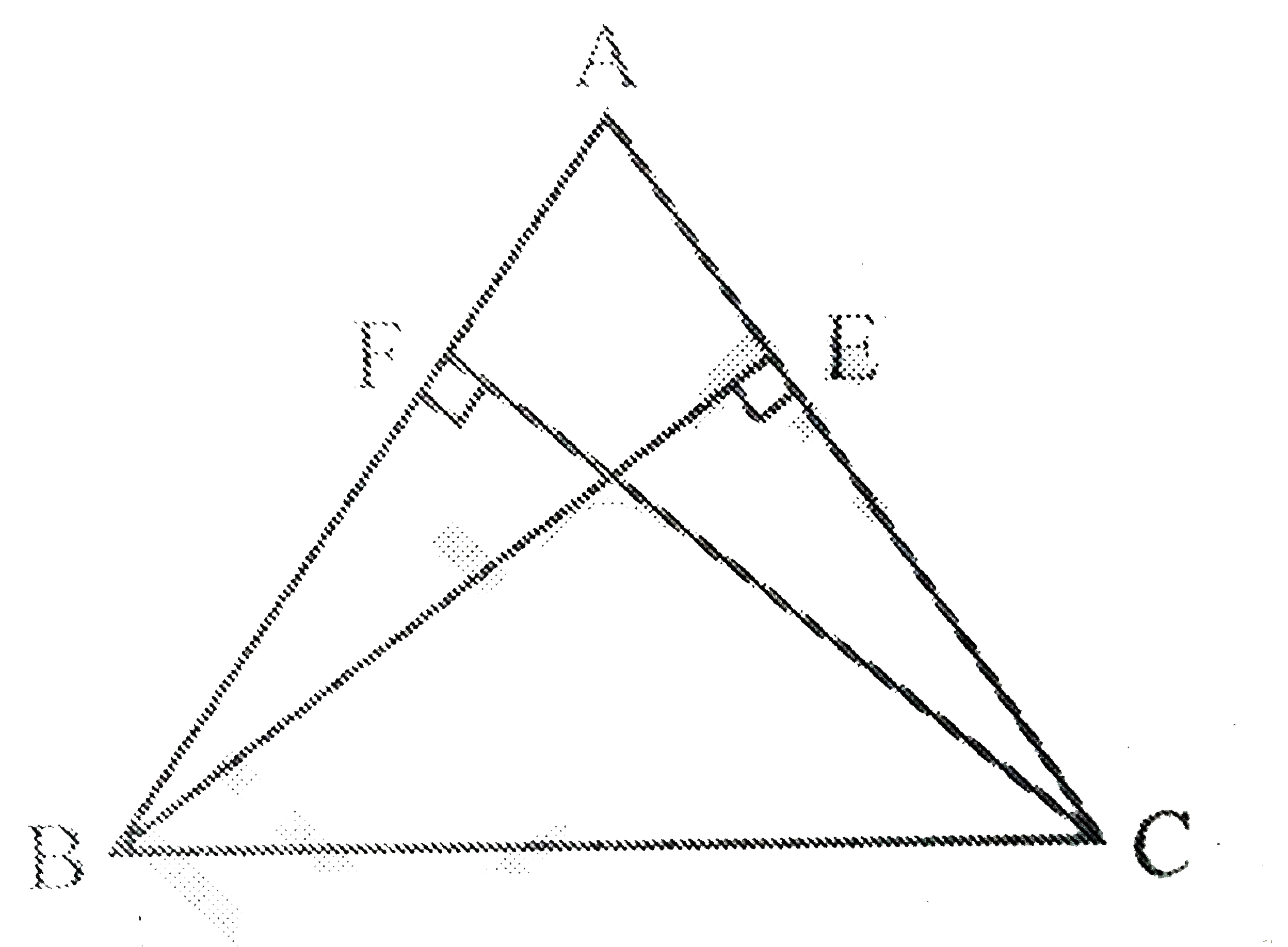Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT ENGLISH-TRIANGLES-EXERCISE 7.2
- In Delta ABC, AD is the perpendicular bisector of BC (see Fig. 7.30)....
Text Solution
|
- ABC is an isosceles triangle in which altitudes BE and CF are drawn t...
Text Solution
|
- In Delta ABC, AB = AC and the bisectors of angles B and C intersect at...
Text Solution
|
- ABC is an isosceles triangle in which A B""=" "A C . Side BA is pr...
Text Solution
|
- A B C is a right angled triangle in which /A=90^0a n d\ A B=A Cdot ...
Text Solution
|
- ABC is a triangle in which altitudes BE and CF to sides AC and AB are...
Text Solution
|
- ABC and DBC are two isosceles triangles on the same base BC (see Fig....
Text Solution
|
- Prove that each angle of an equilateral triangle is 60^0
Text Solution
|