Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT ENGLISH-BIOMOLECULES-Exercise
- Glucose or sucrose are soluble in water but cyclohexane or bezene (sim...
Text Solution
|
- What are the expected products of hydrolysis of lactose ?
Text Solution
|
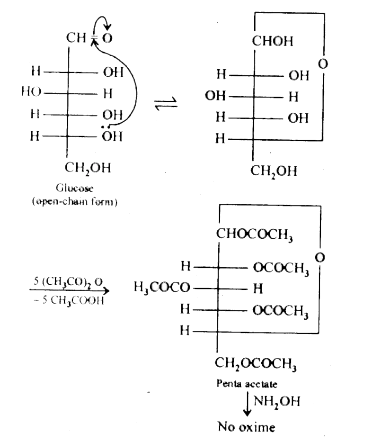
- How do you explain the absence of aldehyde group in the pentaacetate o...
Text Solution
|
- The melting points and solubility in water of amino acids are generall...
Text Solution
|
- Where does the water present in the egg go after boiling the egg ?
Text Solution
|
- Why cannot vitamin C be stored in our body ?
Text Solution
|
- What products would be formed when a nucleotide from DNA containing th...
Text Solution
|
- When RNA is hydrolysed, there is no relationship among the quantities ...
Text Solution
|
- What are monosaccharides?
Text Solution
|
- What are reducing sugars ?
Text Solution
|
- Write two main functions of carbohydrates in plants.
Text Solution
|
- Classify the following into monosaccharides and disaccharides: Ribose,...
Text Solution
|
- What do you understand by the term glycosidic linkage?
Text Solution
|
- What is glycogen? How is it different from starch?
Text Solution
|
- What are the hydrolysis products of (i) sucrose and (ii) lactose?
Text Solution
|
- What is the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose?
Text Solution
|
- What happenes when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents? ...
Text Solution
|
- Enumerate the reactions of D-Glucose which cannot be explained by its ...
Text Solution
|
- What are the essential and non-essential amino acids?Give two examples...
Text Solution
|
- Define the following as related to proteins: (i) Peptide linkage (...
Text Solution
|