Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
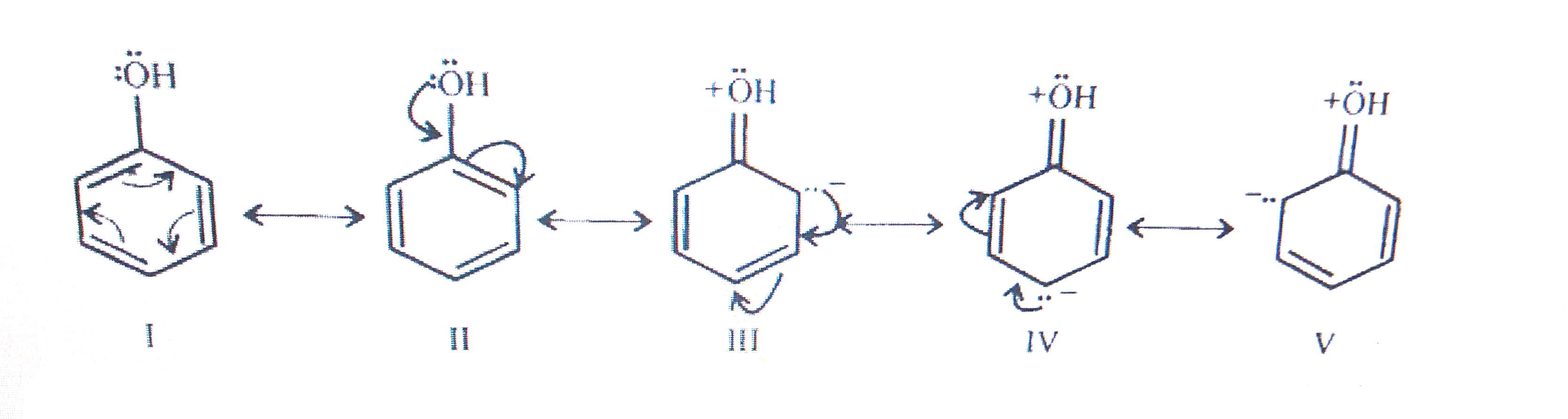
- Explain how does the (---OH) group attached to a carbon of benzene rin...
Text Solution
|
- Explain how does the (---OH) group attached to a carbon of benzene rin...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following group activates the benzene ring most towards e...
Text Solution
|
- समझाइए की बेंज़ीन वलय से जुड़ा -OH समूह उसे इलेक्ट्रोनरागी प्रतिस्थापन क...
Text Solution
|
- समझाइए कि बेन्जीन वलय से जुड़ा-OH समूह उसे इलेक्ट्रॉनरागी प्रतिस्थापन ...
Text Solution
|
- व्याख्या कीजिए की किस प्रकार बैंजीन रिंग के एक कार्बन से जुड़ा -OH समूह...
Text Solution
|
- Explain OH group attached to benzene ring activates it towards electro...
Text Solution
|
- समझाइये कि बेंजीन रिंग पर जुडी कार्बन पर जुड़ा -OH समूह उसको इलेक्ट्रोस...
Text Solution
|
- समझाइए कि बैंजीन वलय से जुड़ा -OH समहू उसे एलेक्ट्रोनंरागी प्...
Text Solution
|