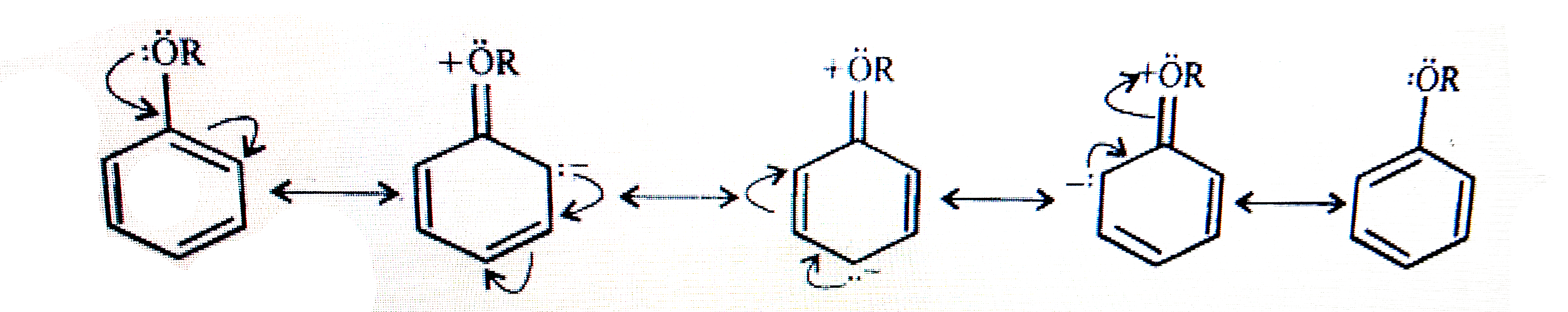Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Explain the fact that in aryl ethers, (i) the alkoxy group activates t...
Text Solution
|
- A group which deactivates the benzene ring towards electrophilic subst...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the fact that in alkyl aryl ethers, alkoxy group : (i) activ...
Text Solution
|
- Alkoxy group attached to benzene ring is ortho and para directing. Jus...
Text Solution
|
- एरिल ऐल्किल ईथरो में निम्न तथ्यों की व्याख्या कीजिए: (i) ऐल्कॉक्सी स...
Text Solution
|
- Expalin (i) the - OH group attached to aromatic eing in phenols and (i...
Text Solution
|
- निम्न तथ्यों की व्याख्या कीजिए- (i) ऐल्कॉक्सी समूह बैंजीन रिंग को इल...
Text Solution
|
- Explain OH group attached to benzene ring activates it towards electro...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the fact that in aryl alkyl ethers the alkoxy group activates ...
Text Solution
|