Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT ENGLISH-RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS-Exercise
- A 4.5 cm needle is placed 12 cm away from a convex mirror of focal len...
Text Solution
|
- A tank is filled with water to a height of 12.5 cm. The apparent depth...
Text Solution
|
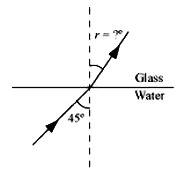
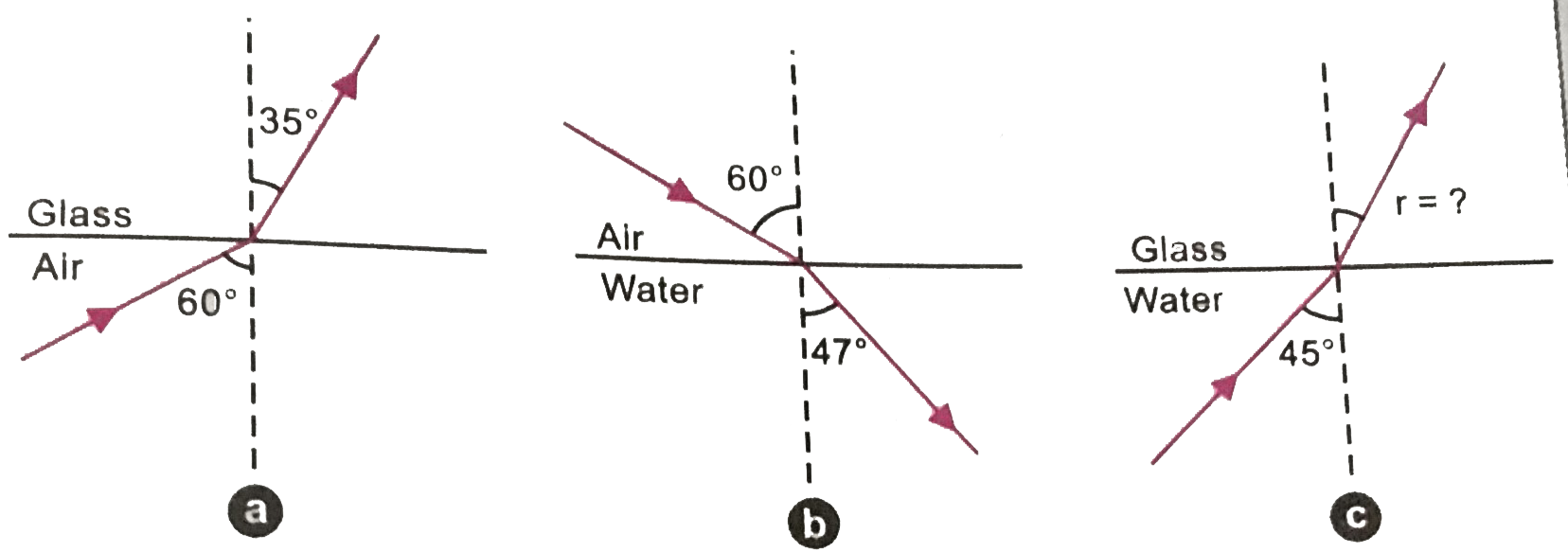
- Fig. (a) and (b) show refraction of an incident ray in air at 60^@ wit...
Text Solution
|
- A small bulb (assumed to be a point source) is placed at the bottom of...
Text Solution
|
- A prism is made of glass of unknown refractive index. A parallel beam ...
Text Solution
|
- A double convex lens is made of glass of refractive index 1.55 with bo...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of light converges to a point P.A lens is placed in the path of...
Text Solution
|
- An object of size 3.0 cm is placed 14 cm in front of a concave lens of...
Text Solution
|
- What is the focal length of a convex lens of focal length 30 cm in con...
Text Solution
|
- A compound microscope consists of an objects lens of focal length 2.0 ...
Text Solution
|
- A person with a normal near point (25 cm) using a compound microscope ...
Text Solution
|
- A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length 144 cm and an ...
Text Solution
|
- (i) A giant refracting telescope at an observatory has an objective le...
Text Solution
|
- Use the mirror equation to deduct that : (a) an object between f and...
Text Solution
|
- A small pin fixed on a table top is viewed from above from a distance ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Fig. shows a cross-section of a 'light pipe' made of a glass fibre...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following questions : Does the apparent depth of a tank o...
Text Solution
|
- The image of a small electric bulb fixed on the wall of a room is to b...
Text Solution
|
- A screen is placed 90 cm from an object. The image of the object on th...
Text Solution
|
- a) Determine the effective focal length of the combination of the two ...
Text Solution
|
 .
.