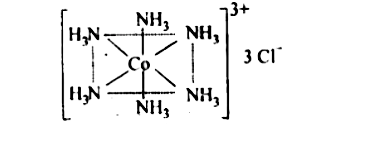
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT ENGLISH-COORDINATION COMPOUNDS-Exercise
- Predict the number of unpaired electrons in the square planar [Pt(CN)4...
Text Solution
|
- The hexaquo manganese(II) ion contains five unpaired electrons, while ...
Text Solution
|
- WERNER’S THEORY OF COORDINATION COMPOUNDS
Text Solution
|
- FeSO4 solution mixed with (NH4)2SO4 solution is 1:1 molar ratio gives ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain with two examples each of the following: coordination entity, ...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by unidentate and ambidentate ligands? Give two examples...
Text Solution
|
- Specify the oxidation numbers of the metals in the following coordinat...
Text Solution
|
- Using IUPAC norms write the fomulas for the following (i). Tetrahydr...
Text Solution
|
- Using IUPAC norms write the systematic names of the following: (i). ...
Text Solution
|
- List various types of isomerism possible for coordination compounds, g...
Text Solution
|
- How many geometrical isomers are possible in the following corrdinatio...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the structures of optical isomers of: (i). [Cr(C2O4)3]^(3-) (...
Text Solution
|
- Draw all the isomers (geometrical and optical) of: (i) [CoCl(2)(en)(...
Text Solution
|
- Write all the geometrical isomers of [Pt(NH3)(Br)(Cl)(py)] and how man...
Text Solution
|
- Aqueous copper sulphate solution (blue in colour) gives: (i). A gree...
Text Solution
|
- What is the coordination entity formed when excess of aqueous KCN is a...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entities o...
Text Solution
|
- Draw figure to show the splitting of d orbitals in an octahedral cryst...
Text Solution
|
- What is spectrochemical series? Explain the difference between a weak ...
Text Solution
|
- The magnitude of CFSE (Crystal Field Splitting Energy , Delta(0)) can ...
Text Solution
|