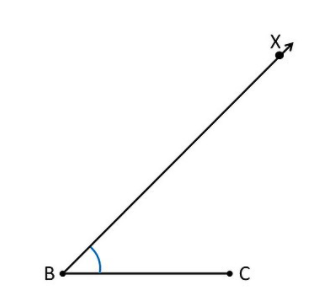
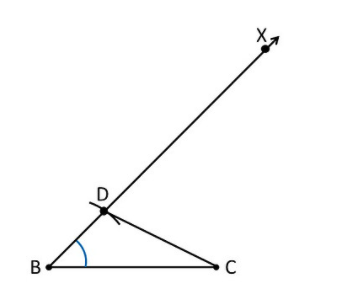
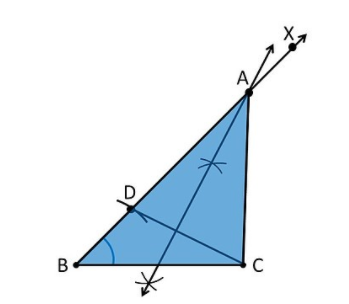
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT ENGLISH-CONSTRUCTIONS-EXERCISE 11.2
- To construct a triangle given its base, a base angle and the differenc...
Text Solution
|
- Construct a triangle ABC in which BC = 7cm, angleB=75^@ and AB + AC = ...
Text Solution
|
- Construct a triangle ABC in which BC = 8cm, angleB=45^@ and AB - AC = ...
Text Solution
|
- Construct a triangle PQR in which QR = 6cm, angleQ=60^@ and PR – PQ = ...
Text Solution
|
- Construct a triangle X Y Z in which /Y=30^0,\ /Z=90^0\ a n d\ \ X Y+...
Text Solution
|
- Construct a right triangle whose base is 12 c m\ and sum of its...
Text Solution
|