Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
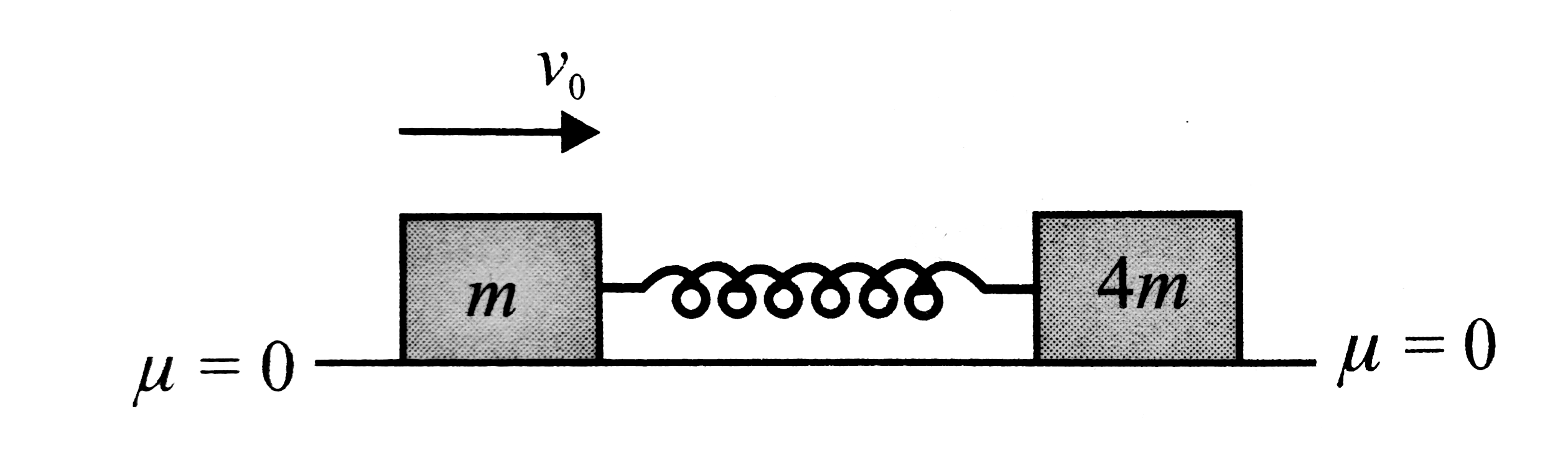
- Two blocks of masses in and 4m lie on a smooth horizontal surface conn...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses in and 4m lie on a smooth horizontal surface conn...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical particles A & B of mass m=2kg is connected at the end of...
Text Solution
|
- Two ring of mass m and 2m are connected with a light spring and can sl...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B of the same mass are connected to a light spring an...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B of masses m & 2m placed on smooth horizontal surfac...
Text Solution
|
- In the fig 4.24 a block of mass m moves with velocity v(0) toward a st...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a smooth block of mass M = m with the h...
Text Solution
|
- The two blocks A and B of same mass connected to a spring and placed o...
Text Solution
|