Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
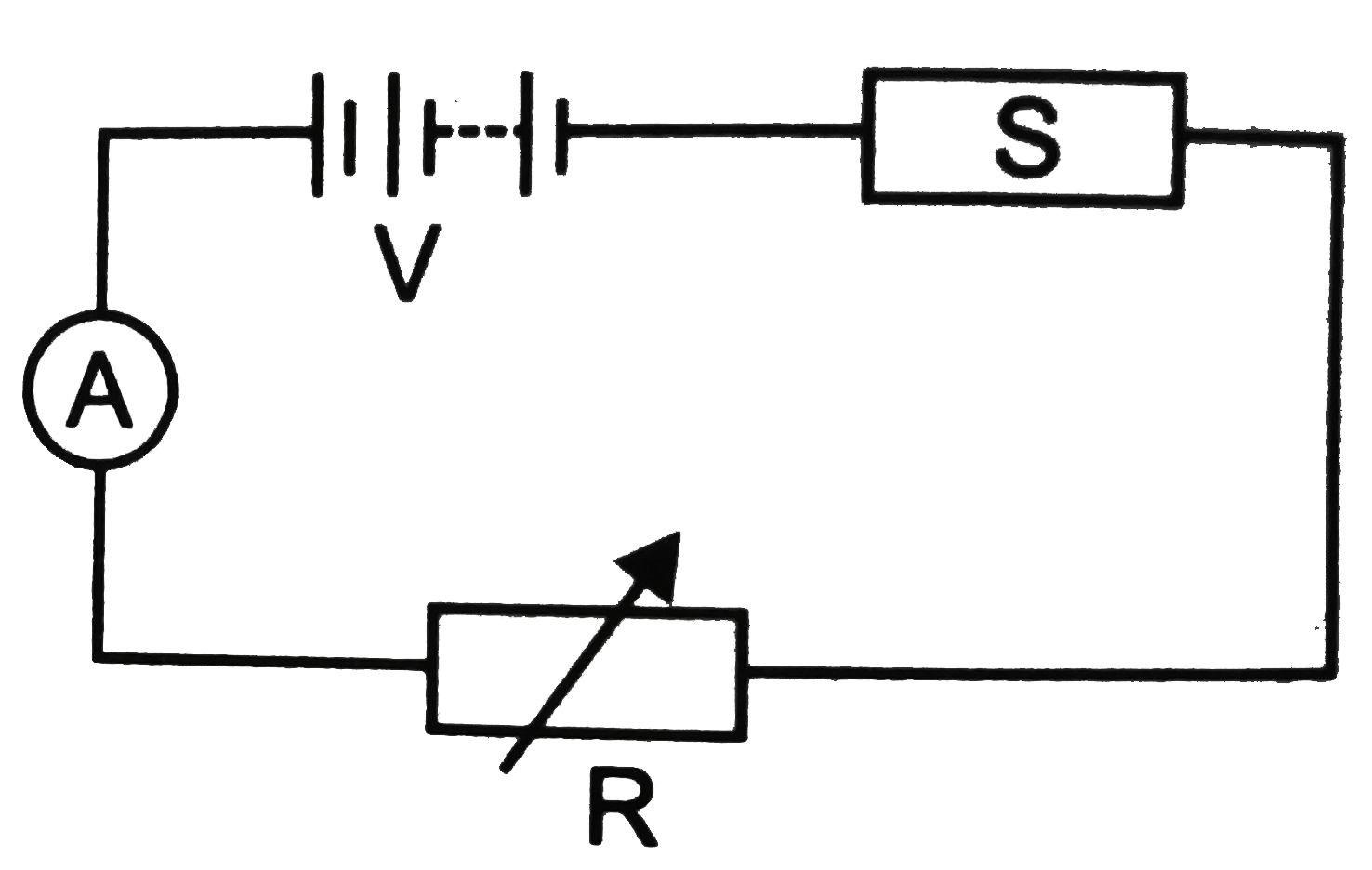
- Figure shows a piece of semiconductor (pure one) S in series with a va...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a piece of semiconductor (pure one) S in series with a va...
Text Solution
|
- The diagram Fig.12 shown a piece of pure semiconductor S in series wit...
Text Solution
|
- If the current supplied to a variable resistor is constant, draw a gra...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a conducting disc rotating about its axis in a perpendicu...
Text Solution
|
- A source of constant voltage V is connected to a resistance R and two ...
Text Solution
|
- If r and s are variables satisfying the equation (1)/(r+s) =1/r+1/s. ...
Text Solution
|
- IF the current supplied to a variable resistor is constant, draw a gra...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र में प्रदर्शित परिपथ में S एक शुद्ध अर्ध-चालक का टुकड़ा है, V एक ब...
Text Solution
|