Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SOLID STATE
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise TOPIC -2 (VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS )|23 VideosSample Paper 8
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise EXCERSICE|54 VideosSOLUTIONS
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise TOPIC - 3 COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES , DETERMINATION OF MOLAR MASS, ABNORMAL MOLAR MASS, VAN.T HOFF FACTOR (LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS - II)|18 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OSWAAL PUBLICATION-SOLID STATE-TOPIC -2 (SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS)
- Give any two differences between Frenkel and Schottky defects.
Text Solution
|
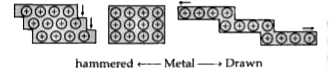
- Based on electron gas theory explain why metals are malleable.
Text Solution
|
- Account for the malleability and ductility of metals on the basis of e...
Text Solution
|
- Based on electron gas theory explain why metals are malleable.
Text Solution
|
- Describe the one major type of semiconductors and contrast their condu...
Text Solution
|
- Define antiferromagnetism with example.
Text Solution
|
- Define ferrimagnetism with suitable examples.
Text Solution
|
- Examine the given defective crystal and {:(A^(+),B^(-),A^(+),B^(-),A...
Text Solution
|
- (i) What type of non-stoichiometric point defect is responsible for th...
Text Solution
|
- How will you distinguish between the following pairs of terms : Tetr...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Write the type of magnetism observed when the magnetic moments are...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Write the type of magnetism observed when the magnetic moments are...
Text Solution
|
- Account for the following : (i) Schottky defects lower the density o...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Why does presence of excess of lithium makes LiCl crystals pink ? ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) What change occurs when AgCl is doped with CdCl(2) ? (b) What ty...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following terms with suitable examples : Ferromagnetism an...
Text Solution
|
- What is a semiconductior ? Give names the two main types of Semi-condu...
Text Solution
|
- What are intrinsic semiconductors ? Give an example.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the Schottky defect terms with suitable examples.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the 12-16 compounds terms with one suitable example :
Text Solution
|