Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- One side of spring of initial, instreached length l(0) = 1m, lying on ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2.0 kg is moving on a frictionless horizontal surface ...
Text Solution
|
- One side of spring of initial, instreached length l(0) = 1m, lying on ...
Text Solution
|
- One end of an ideal spring of unstreched length l(O)=1m , is fixed on ...
Text Solution
|
- One end of an ideal spring of unstreched length l(O)=1m, is fixed on a...
Text Solution
|
- One end of an ideal spring of unstreched length l(O)=1m , is fixed on ...
Text Solution
|
- Mass m is connected with an ideal spring of natural length l whose oth...
Text Solution
|
- If the system is suspended by the mass m the length of the spring is l...
Text Solution
|
- During hockey practice, two pucks are sliding across the ice in the sa...
Text Solution
|
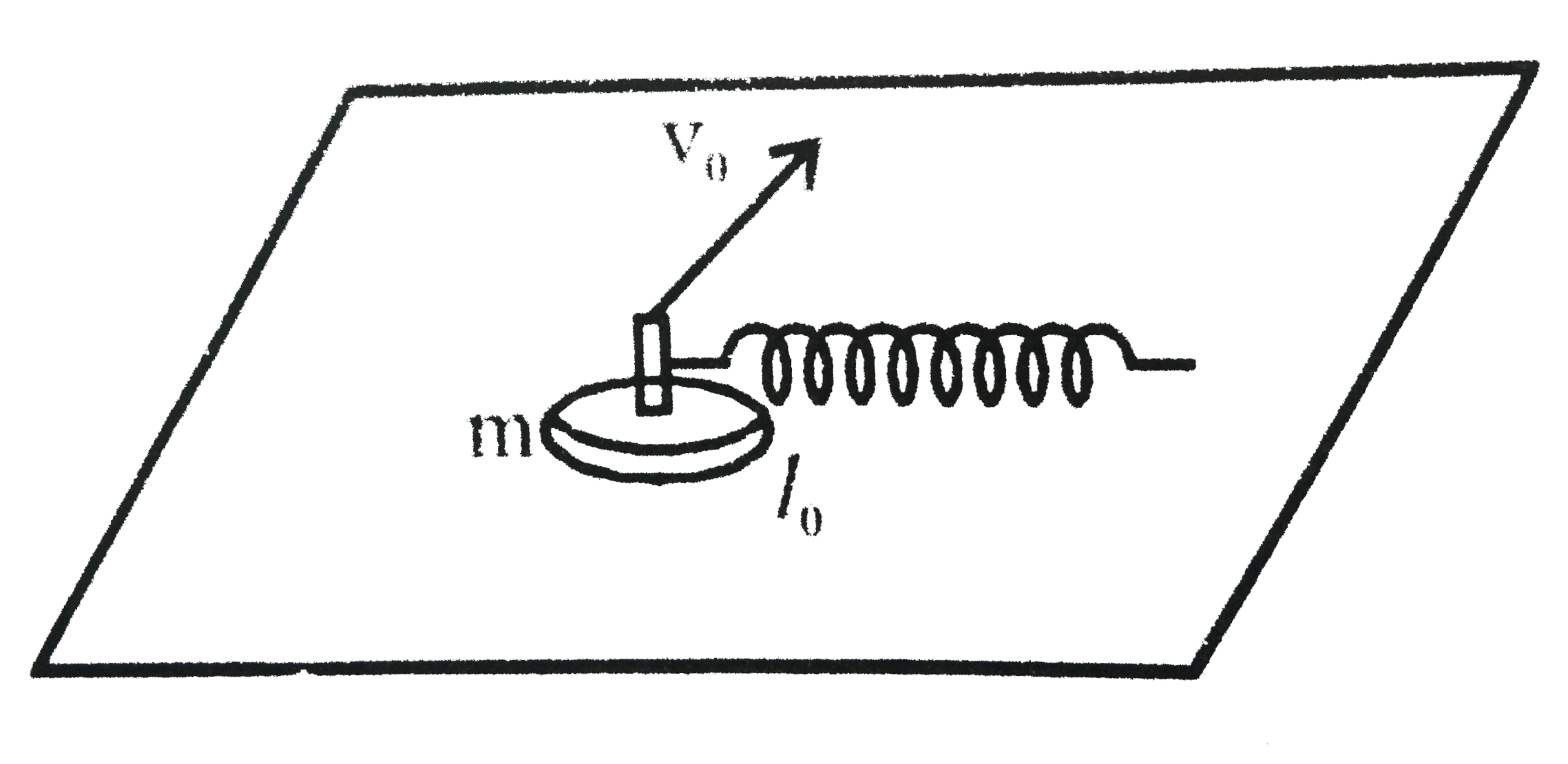 .
.