Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
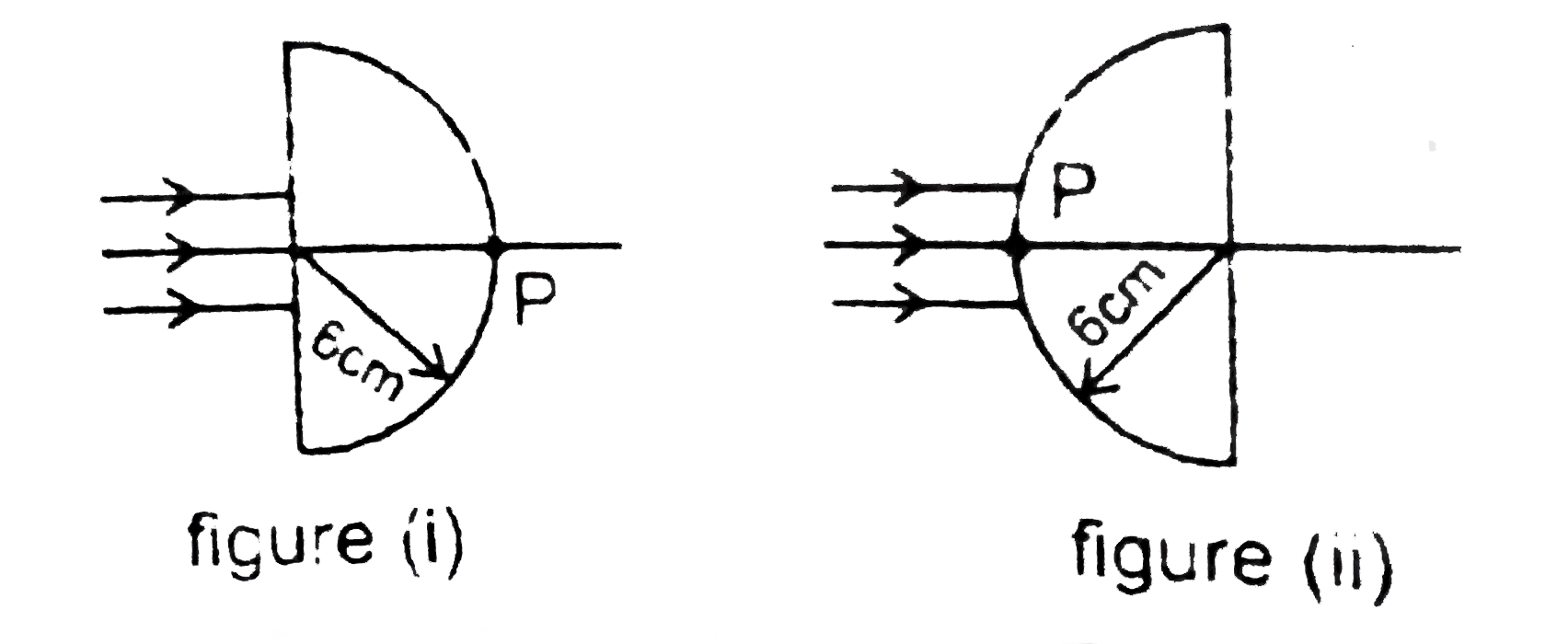
- A parallel beam of light is incident normally on the flat surface of a...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel narrow beam of light is incident on the surface of a transp...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light travelling in water (refractive index =4//3) ...
Text Solution
|
- When a ray of light is incident normally on one refracting surface of ...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light is incident normally on the flat surface of a...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light is incident on the surface of a transparent h...
Text Solution
|
- A converging beam of light rays incident on a glasa-air interface as s...
Text Solution
|
- A paraxial beam is incident on a glass (n=1.5) hemisphere of radius R=...
Text Solution
|
- प्रकाश है एक किरण काँच के समतल टुकड़े पर गिरती है जिसका अपवर्तनांक 1.62...
Text Solution
|
 .
.