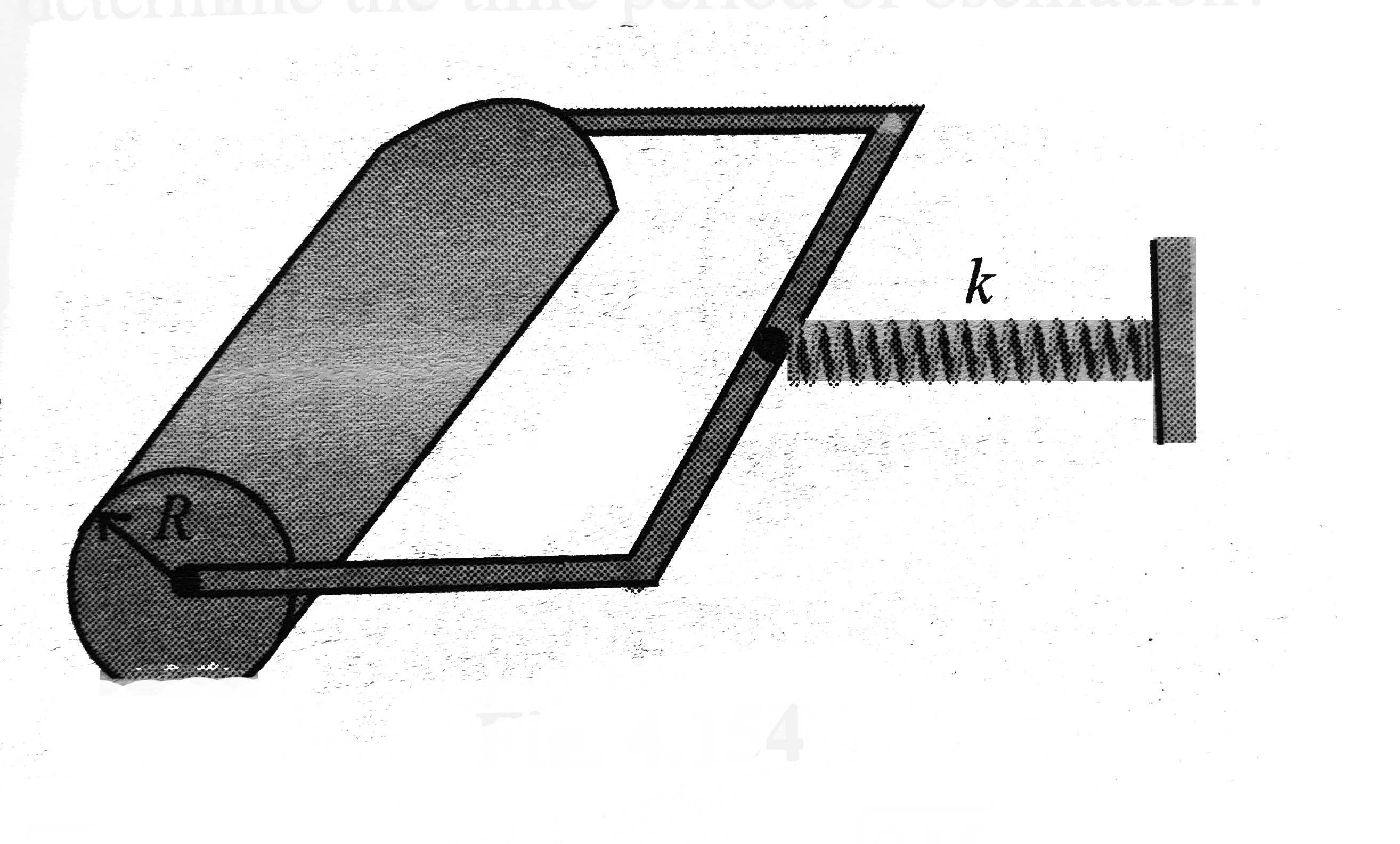Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A soil cylinder of mass M and radius R is connected to a spring as sho...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform solid cylinder of mass m and radius R is placed on a rough h...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform cylinder of mass M and radius R is released from rest on a r...
Text Solution
|
- A soil cylinder of mass M and radius R is connected to a spring as sho...
Text Solution
|
- A solid cylinder of mass M and radius R pure rolls on a rough surface ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid uniform cylinder of mass M attached to a massless spring of fo...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder of mass M and radius R lies on a plank of mass M as shown. ...
Text Solution
|
- Two uniform cylinders, each of mass m = 10 kg and radius r = 150 mm, a...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder is rotating with angular velocity omega(0) and is gently pu...
Text Solution
|