Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
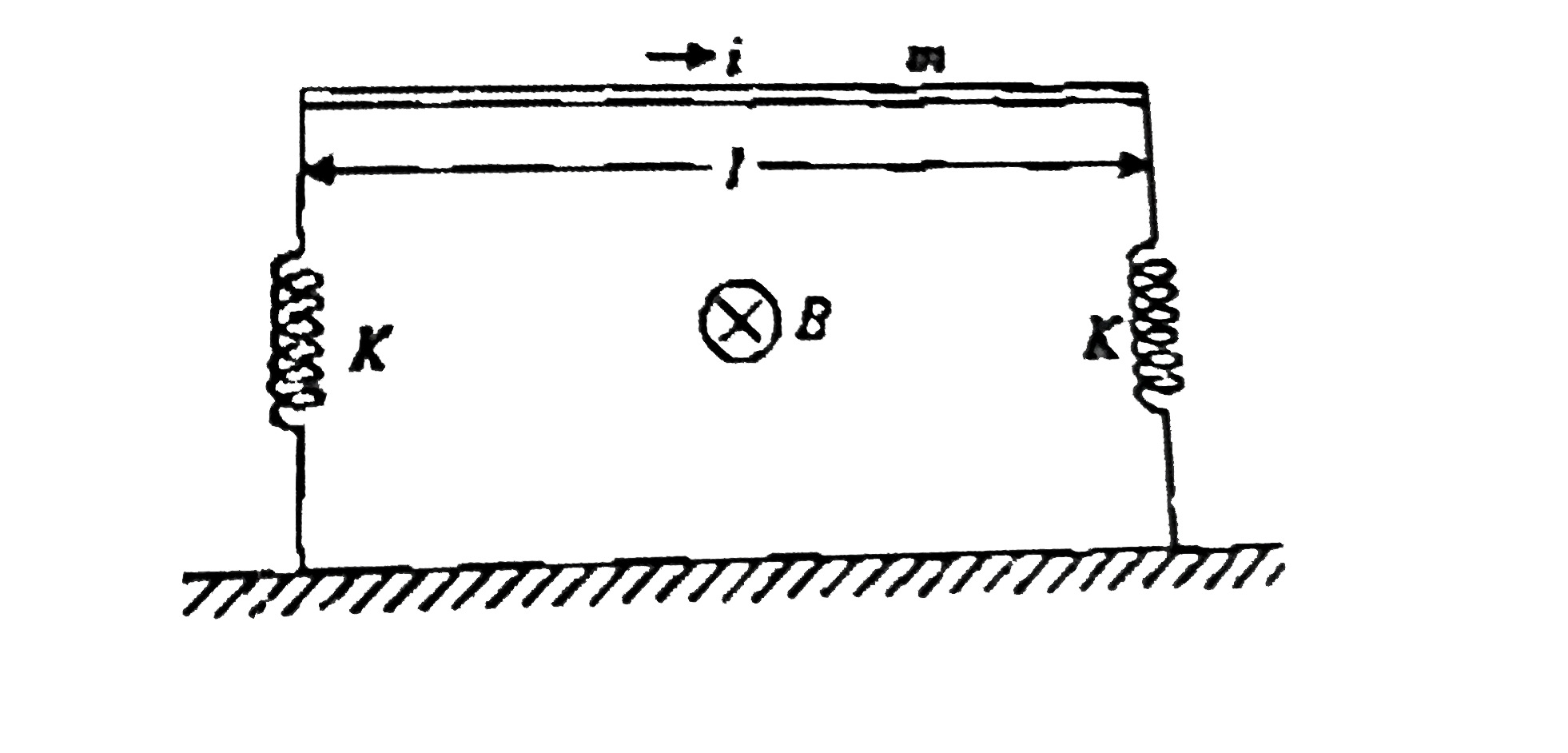
- A horizontal metallic rod of mass 'm' and length 'l' is supported by t...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length l and mass m, pivoted at one end, is held by a spring ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of length L and mass M is pivotedat the centre. Its two ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of mass m and length L is kept on a horizontal smooth surface. T...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal metallic rod of mass 'm' and length 'l' is supported by t...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal metallic rod of mass m and length l is supported by two v...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown a uniform conducing rod of mass m and length l is ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown a uniform conducing rod of mass m and length l is ...
Text Solution
|
- लम्बाई L तथा द्रव्यमान M की एकसमान छड़ अपने केंद्र पर कीलकित है। इसके द...
Text Solution
|