Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
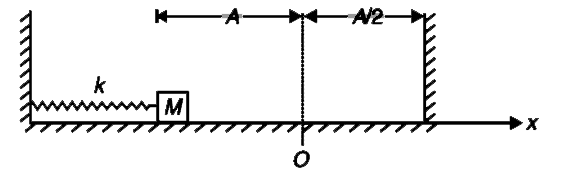
- A block of mass M connected to an ideal spring of force constant k, is...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a smooth track, a part of which is a circle of radius r. ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shown a block P of mass m resting on a smooth horizontal surfac...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m length force a verical of spring constant k If the b...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M connected to an ideal spring of force constant k, is...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M = 40 kg is released on a smooth incline from point A...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is pushed up against a spring, compressing it a dist...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, the block of mass m, attached to the spring of stiffnes...
Text Solution
|
- The block of mass m is released when the spring was in its natrual len...
Text Solution
|