Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
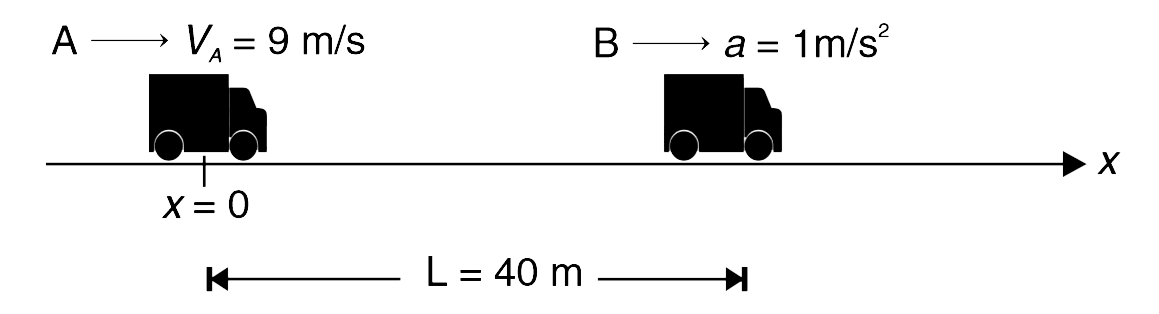
- There are two cars on a straight road, marked as x axis. Car A is trav...
Text Solution
|
- Car A and car B start moving simultaneously in the same direction alon...
Text Solution
|
- Two cars A and B of equal masses (100 Kg) are moving on a straight hor...
Text Solution
|
- There are two cars on a straight road, marked as x axis. Car A is trav...
Text Solution
|
- A car is moving on a straight road. The velocity of the car varies wit...
Text Solution
|
- When a motorcyle moving with a unifrom speed 11 m/s is at a distance 2...
Text Solution
|
- A car travels from rest with a constant acceleration "a" for "t" secon...
Text Solution
|
- Car A and car B start moving simultaneously in the same direction alon...
Text Solution
|
- Two cars A and B are moving on parallel roads in the same direction. C...
Text Solution
|