Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
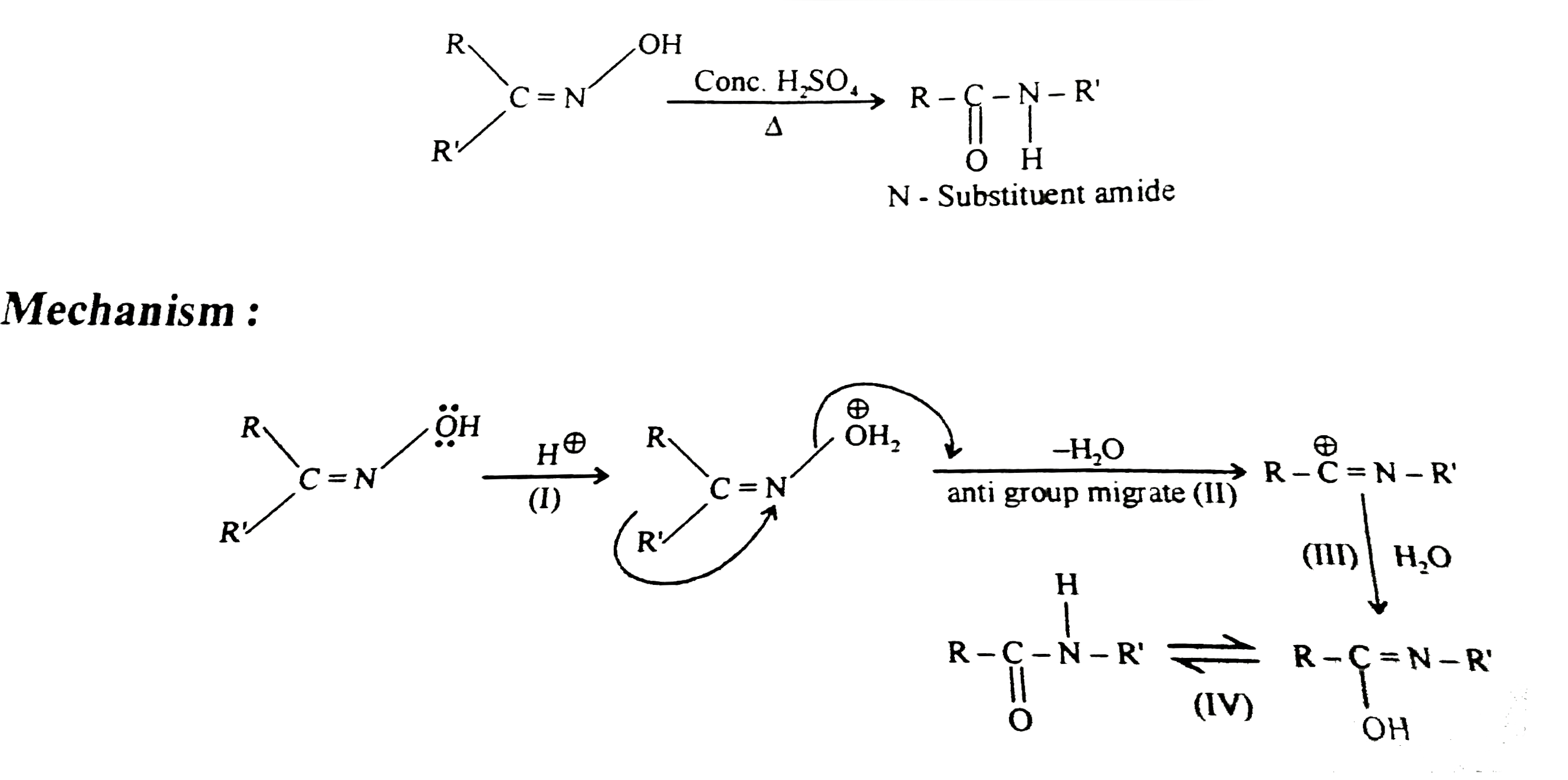
- Ketoxine when heated with certain reagents undergoes rearrangement to ...
Text Solution
|
- Ketoxine when heated with certain reagents undergoes rearrangement to ...
Text Solution
|
- Ketoxine when heated with certain reagents undergoes rearrangement to ...
Text Solution
|
- Ketoxine when heated with certain reagents undergoes rearrangement to ...
Text Solution
|
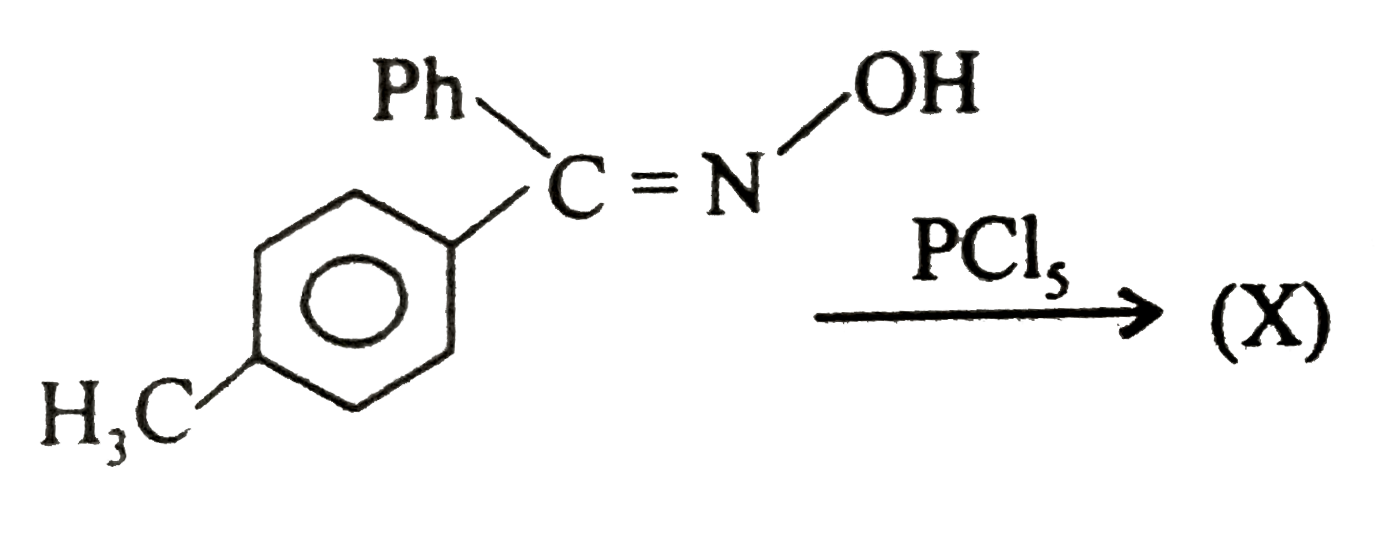
- Ketoxime when heated with certain reagents undergoes rearrangement to ...
Text Solution
|
- Ketoxime when heated with certain reagents undergoes rearrangement to ...
Text Solution
|
- Ketoxime when heated with certain reagents undergoes rearrangement to ...
Text Solution
|
- Rearrangement of an oxime to an amide in the presence of strong acid i...
Text Solution
|
- Caprolactum is monomer for the manufacture of nylon-6 and is obtained ...
Text Solution
|