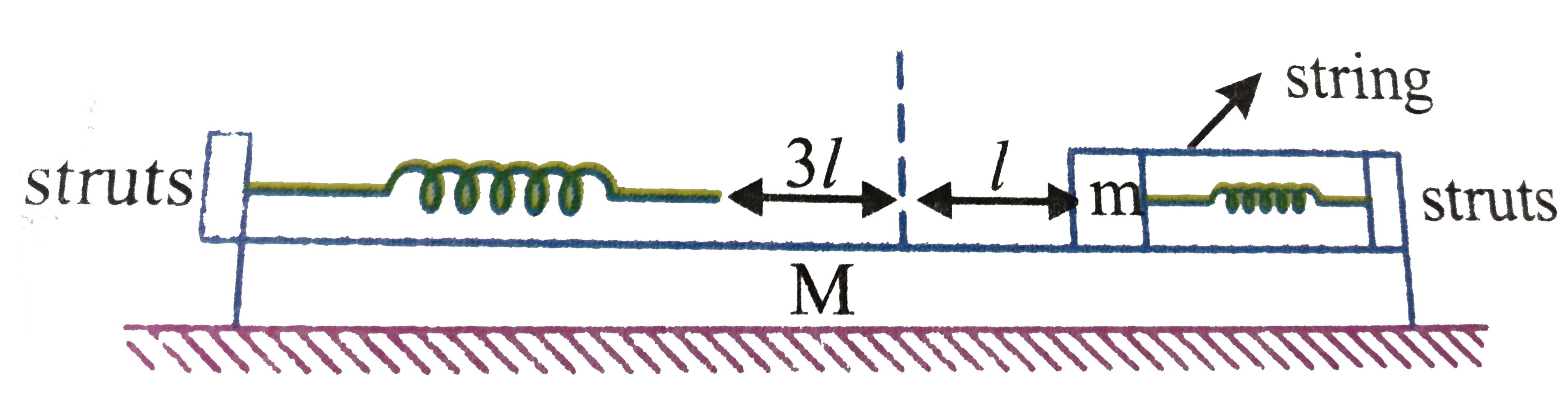
A plank of mass `M` is placed on a smooth hroizonal surface. Two light identical springs each of stiffness `k` are rigidly connected to structs at the ends of the plank as shown. When the spring are in their unextended position the distance between their free ends is `3l`. a block of mass `m` is placed on the plank and pressed aganist one of the springs so that it is compressed by `l`. To keep the blocks at rest it is connected to the strut by means of a light string, initially the syetem is at rest. Now the string is burnt.
Maximum displacement of plank is:
A plank of mass `M` is placed on a smooth hroizonal surface. Two light identical springs each of stiffness `k` are rigidly connected to structs at the ends of the plank as shown. When the spring are in their unextended position the distance between their free ends is `3l`. a block of mass `m` is placed on the plank and pressed aganist one of the springs so that it is compressed by `l`. To keep the blocks at rest it is connected to the strut by means of a light string, initially the syetem is at rest. Now the string is burnt.

Maximum displacement of plank is:

Maximum displacement of plank is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A plank of mass M is placed on a smooth hroizonal surface. Two light identical springs each of stiffness k are rigidly connected to structs at the ends of the plank as shown. When the spring are in their unextended position the distance between their free ends is 3l . a block of mass m is placed on the plank and pressed aganist one of the springs so that it is compressed by l . To keep the blocks at rest it is connected to the strut by means of a light string, initially the syetem is at rest. Now the string is burnt. Time period of oscillation of block:
According to the principle of conservation of linear momentum if the external force acting on the system is zero, the linear momentum of the system will remain conserved. It means if the centre of mass of a system is initially at rest, it will remain at rest in the absence of external force, that is, the displacement of centre of mass will be zero. A plank of mass M is placed on a smooth horizontal surface. light identical springs, each of stiffness K , are rigidly connected to struts at the end of the plank as shown in Fig. When the springs are in their unextended position, the distance between their free ends is 3l . A block of mass m is placed on the plank and pressed against one of the springs so that it is compressed to l . To keep the block at rest it is connected to the strut means of a light string. Initially, the system is at rest, Now the string is burnt. The maximum displacement of the plank is
According to the principle of conservation of linear momentum if the external force acting on the system is zero, the linear momentum of the system will remain conserved. It means if the centre of mass of a system is initially at rest, it will remain at rest in the absence of external force, that is, the displacement of centre of mass will be zero. A plank of mass M is placed on a smooth horizontal surface. light identical springs, each of stiffness K , are rigidly connected to struts at the end of the plank as shown in Fig. When the springs are in their unextended position, the distance between their free ends is 3l . A block of mass m is placed on the plank and pressed against one of the springs so that it is compressed to l . To keep the block at rest it is connected to the strut means of a light string. Initially, the system is at rest, Now the string is burnt. The maximum velocity of the plank is
According to the principle of conservation of linear momentum if the external force acting on the system is zero, the linear momentum of the system will remain conserved. It means if the centre of mass of a system is initially at rest, it will remain at rest in the absence of external force, that is, the displacement of centre of mass will be zero. A plank of mass M is placed on a smooth horizontal surface. light identical springs, each of stiffness K , are rigidly connected to struts at the end of the plank as shown in Fig. When the springs are in their unextended position, the distance between their free ends is 3l . A block of mass m is placed on the plank and pressed against one of the springs so that it is compressed to l . To keep the block at rest it is connected to the strut means of a light string. Initially, the system is at rest, Now the string is burnt. The maximum kinetic energy of the block m is
According to the principle of conservation of linear momentum if the external force acting on the system is zero, the linear momentum of the system will remain conserved. It means if the centre of mass of a system is initially at rest, it will remain at rest in the absence of external force, that is, the displacement of centre of mass will be zero. A plank of mass M is placed on a smooth horizontal surface. light identical springs, each of stiffness K , are rigidly connected to struts at the end of the plank as shown in Fig. When the springs are in their unextended position, the distance between their free ends is 3l . A block of mass m is placed on the plank and pressed against one of the springs so that it is compressed to l . To keep the block at rest it is connected to the strut means of a light string. Initially, the system is at rest, Now the string is burnt. The maximum kinetic energy of the block m is
A wooden plank of mass 20kg is resting on a smooth horizontal floor. A man of mass 60kg starts moving from one end of the plank to the other end. The length of the plank is 10m . Find the displacement of the plank over the floor when the man reaches the other end of the plank.
A wooden plank of mass 20kg is resting on a smooth horizontal floor. A man of mass 60kg starts moving from one end of the plank to the other end. The length of the plank is 10m . Find the displacement of the plank over the floor when the man reaches the other end of the plank.
A plank of mass 4m is placed on a smooth horizontal surface and a spring of force constant k is attached to the plank, whose other end is fixed on a block of mass m placed over tha plank. All surface are smooth. A bullet of mass m moving with horizontal velocity u strikes the block and gets embeded in it. Choose the correct option for subsequent motion :
A plank of mass 4m is placed on a smooth horizontal surface and a spring of force constant k is attached to the plank, whose other end is fixed on a block of mass m placed over tha plank. All surface are smooth. A bullet of mass m moving with horizontal velocity u strikes the block and gets embeded in it. Choose the correct option for subsequent motion :
Recommended Questions
- A plank of mass M is placed on a smooth hroizonal surface. Two light i...
Text Solution
|
- A planck of mass 5kg is placed on a frictionless horizontal plane. Fur...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is connected rigidly with a smooth wedge (plank) by ...
Text Solution
|
- A spring is connected with plank and other end of spring is connected ...
Text Solution
|
- According to the principle of conservation of linear momentum if the e...
Text Solution
|
- According to the principle of conservation of linear momentum if the e...
Text Solution
|
- According to the principle of conservation of linear momentum if the e...
Text Solution
|
- Block A of mass m is placed on a plank B. A light support S is fixed o...
Text Solution
|
- A plank of mass M is placed on a smooth hroizonal surface. Two light i...
Text Solution
|