Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
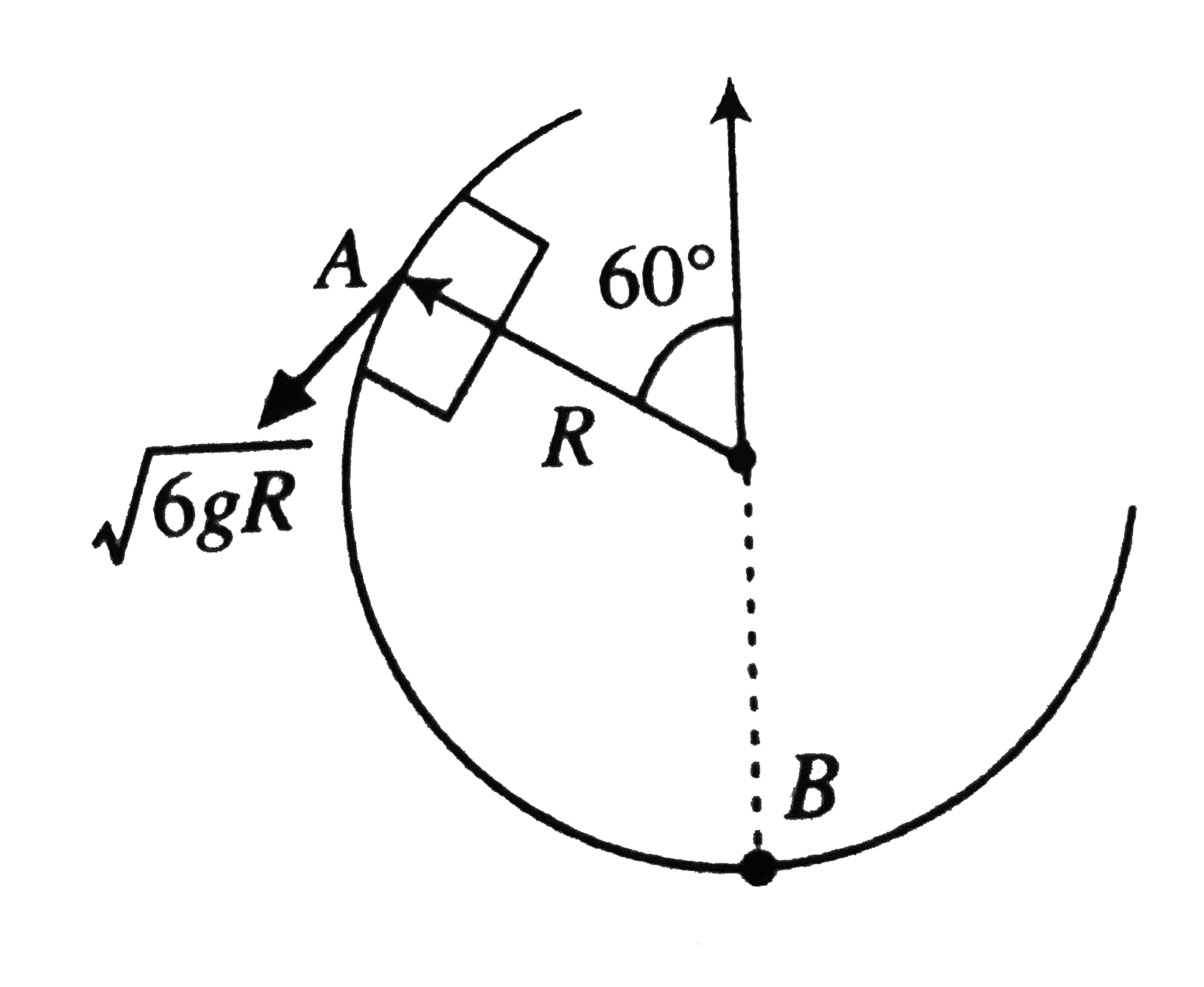
- Figure shows a smooth vertical circular track AB of radius R. A block ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m slides down a smooth vertical circular track. During...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a smooth track, a part of which is a circle of radius r. ...
Text Solution
|
- AOB is a smooth semicircular track of radius r. A block of mass m is g...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a smooth vertical circular track AB of radius R. A block ...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass m is pushed on a smooth track from position A wi...
Text Solution
|
- A block weighing 10 kg travels down a smooth curved track AB joined to...
Text Solution
|
- A block is freely sliding down from a vertical height 4 m on smooth in...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m slides down a smooth vertical circular track. During...
Text Solution
|