Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
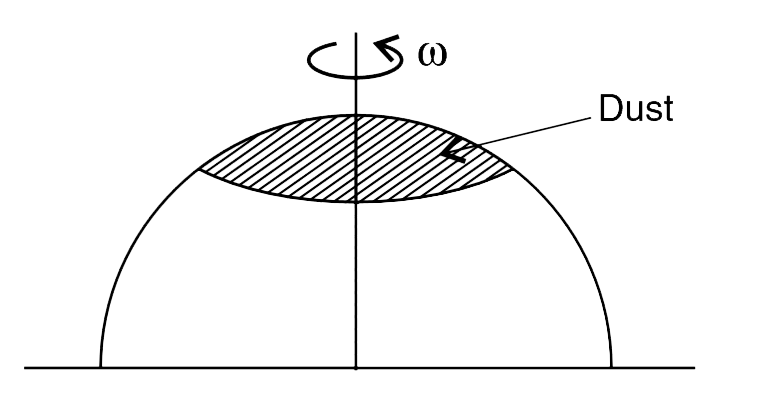
- A metallic hemisphere is having dust on its surface. The sphere is rot...
Text Solution
|
- Surface area of Sphere and Hemisphere
Text Solution
|
- A metal disc of radius R can rotate about the vertical axis passing th...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic hemisphere is having dust on its surface. The sphere is rot...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is placed inside a hemispherical bowl which rotates about i...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge Q is placed at the centre of a hemisphere. Find the rat...
Text Solution
|
- Whole surface area of a solid hemisphere is equal to the curved surfac...
Text Solution
|
- What is the total surface area of hemisphere if the radius of hemisphe...
Text Solution
|
- Curved surface area of a hemisphere = ……………
Text Solution
|