Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
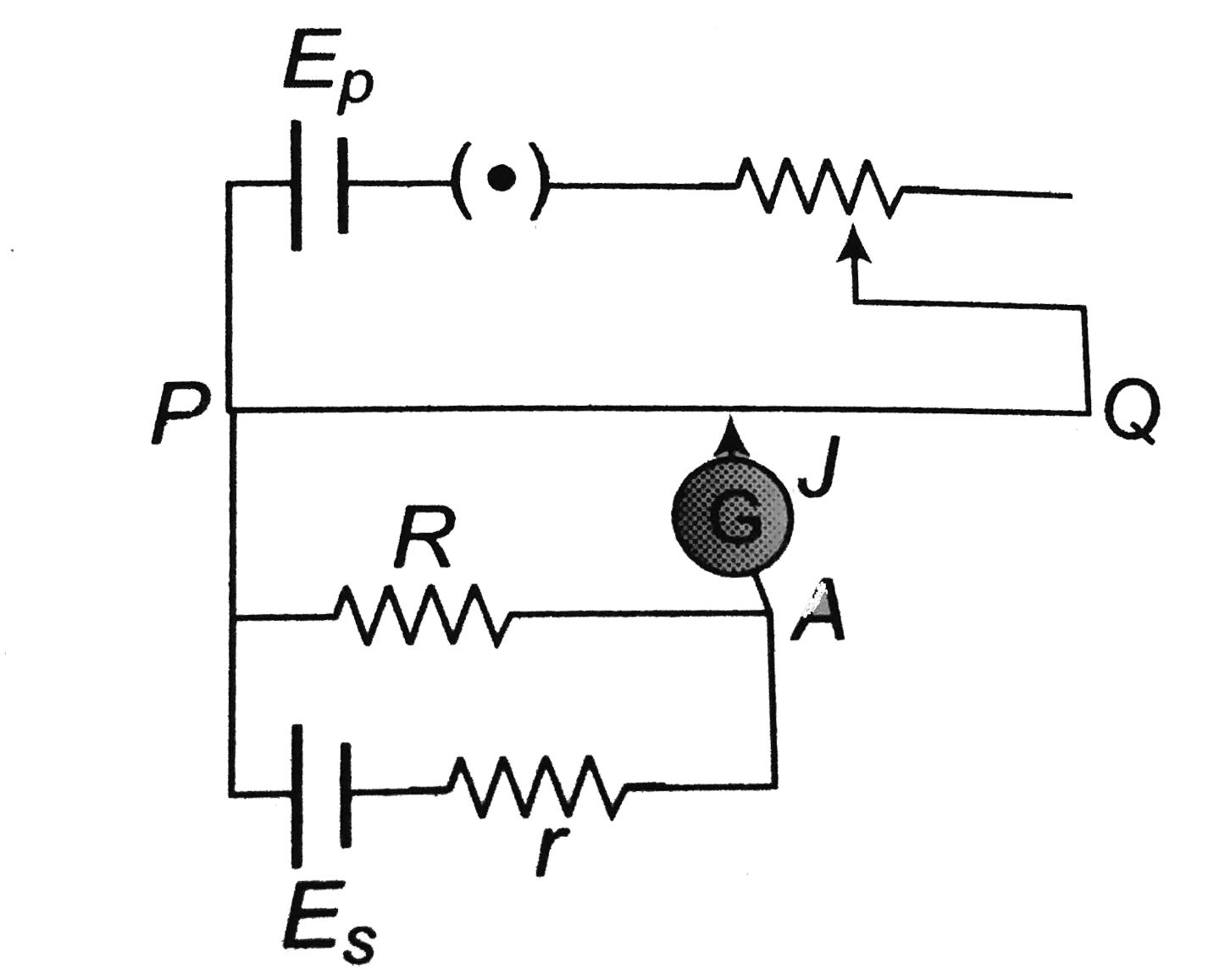
- One of the circuits for the measurement of resistance by potentiometer...
Text Solution
|
- Circuit for the measurement of resistance by potentiometer is shown in...
Text Solution
|
- One of the circuits for the measurement of resistance by potentiometer...
Text Solution
|
- Find the magnitude and direction of the current flowing through the ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, the potentiometer wire of length l = 100 cm and resista...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit diagram given in Fig. 4.31, the cells E(1) " and " E(2)...
Text Solution
|
- In an experiment to determine the resistance of a galvanometer by half...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, the potentiometer wire of length l = 100 cm and resista...
Text Solution
|
- A potentiometer wire PQ of 1 m length is connected to a standard cell ...
Text Solution
|