Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
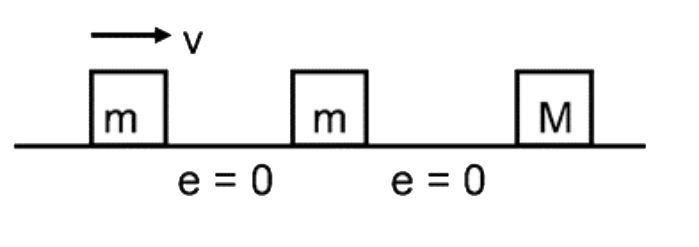
- Three blocks of masses m , m and M are kept on a frictionless floor as...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks are initially placed as shown in the figure. Block A has ...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks are placed on smooth horizontal surface and lie on same h...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet of mass m moving with velocity u on smooth surface strikes a ...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet of mass m moving with velocity v strikes a block of mass M at...
Text Solution
|
- There are hundred indentical blocks equally spaced on a frictionless t...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M=4kg is moving with velocity V=6m/s toward a target b...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks are initially placed as shown in the figure. Block A has ...
Text Solution
|
- Infinite blocks each of mass M are placed along a straight line with a...
Text Solution
|