Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
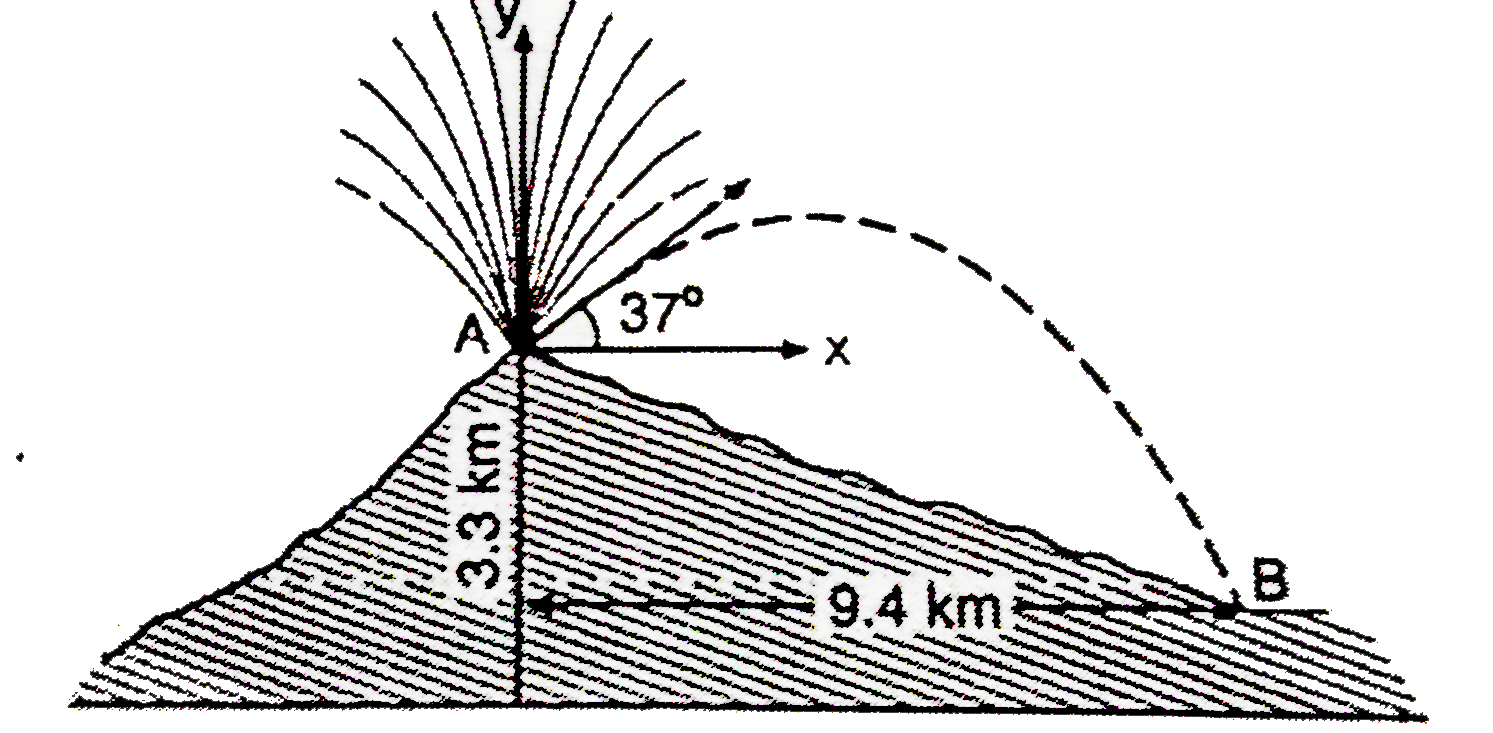
- During volcanic eruption chunks of slid rock are blasted out of the vo...
Text Solution
|
- What is wrong with the speed time graph as shown in Fig.2 (b) .25.
Text Solution
|
- A particle is thrown with speed of 50 m//s at an angle of projection 3...
Text Solution
|
- During volcanic eruption chunks of slid rock are blasted out of the vo...
Text Solution
|
- Statement : Volcanic eruption is accompanied by earthquakes Statemen...
Text Solution
|
- किसी वस्तु को किसी मीनार कि चोटी से गिराया गया- (क) 4.9 m दुरी तक गि...
Text Solution
|
- an object g = 9.8 m//s^2 is falling down with an acceleration of
Text Solution
|
- What do you mean by caldera? (a) Rocks that found in rain forests (b) ...
Text Solution
|
- What do the word volcanism and volcano indicate?
Text Solution
|