Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
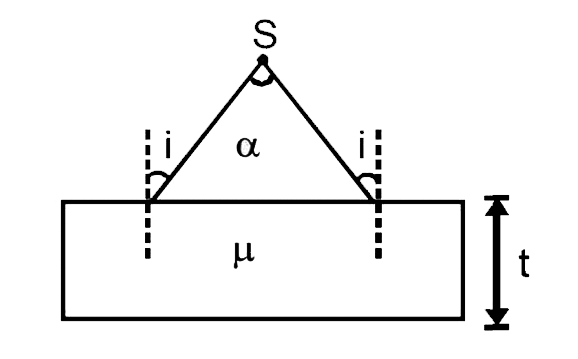
- A diverging beam of light from a point source S having devergence angl...
Text Solution
|
- A diverging beam of light from a point source S having devergence angl...
Text Solution
|
- A diverging beam of light from a point source S having divergence ang...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray is incident at 45^(@) on a glass slab. The slab is 3cm thi...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light falls on a glass slab at an incident angle of 45^(@) an...
Text Solution
|
- एक बिंदु स्रोत S जिसके लिए अपसारी कोण alpha है, से प्राप्त एक अपसारी क...
Text Solution
|
- A diverging beam of rays from a point source S , making a divergent an...
Text Solution
|
- For refraction of light through a glass slab the angle of emergence is...
Text Solution
|
- एक प्रकाश-किरण काँच से वायु में संचरित होती है | (काँच का अपवर्तनांक ...
Text Solution
|