A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMODYANMICS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section-D Ncert Exemplar Solution (Very Short Answer )|5 VideosTHERMODYANMICS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section-D Ncert Exemplar Solution (Short Answer )|6 VideosTHERMODYANMICS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section-D Ncert Exemplar Solution (MCQs)|6 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Question Paper (Section - D) (Answer following in brief :) Each carry 4 marks|1 VideosUNITS AND MEASUREMENT
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section -F (Questions from Module )|20 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-THERMODYANMICS -Section-D Ncert Exemplar Solution (MCQs More than one option )
- Which of the processes described below are irreversible ?
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas undergoes isothermal process from some initial state i to...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows the P- V diagram of an ideal gas undergoing a change of s...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a cycle followed by an engine as shown in figure, 1 to 2 is...
Text Solution
|
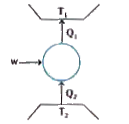
- Consider a heat engine as shown in figure. Q1 and Q2 are heat added bo...
Text Solution
|