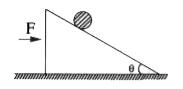
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
LAWS OF MOTION
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise EXERCISE - I|151 VideosLAWS OF MOTION
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise EXERCISE - II|117 VideosLAWS OF MOTION
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise QUESTIONS FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWER|5 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise ADDITIONAL PRACTICE EXERCISE (LEVEL-II PRACTICE SHEET (ADVANCED) INTEGER TYPE QUESTIONS)|6 VideosLOGIC GATES
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Exercise (Very Short Answer)|16 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-LAWS OF MOTION-Application
- A block of mass m kg is pushed up against a wall by a force P that mak...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed behind in contact with vertical side of M ...
Text Solution
|
- A body slides down a rough inclined plane and then over a rough plane ...
Text Solution
|
- A body takes ''n'' times as much time to slide down a rough inclined p...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, the wedge is acted upon by a constant horizontal ...
Text Solution
|
- A body is released from rest from the top of an inclined plane of leng...
Text Solution
|