Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION D (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQS)) (MCQS FROM .DARPAN. BASED ON TEXTBOOK) (ELECTROSTATIC ELECTRIC CHARGE AND FRICTIONAL ELECTRICAL CHARGE)|55 VideosELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION D (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQS)) (MCQS FROM .DARPAN. BASED ON TEXTBOOK) (LECTRIC FIELD AND ELECTRIC DIPOLE)|26 VideosELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION C NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION (SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS)|6 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section-D (MCQs asked in GUJCET/Board Exam)|1 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section D MCQs (MCQs asked in Competitive Exams )|38 Videos
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS -SECTION C NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION (LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS)
- In 1959 Lyttleton and Bondi suggested that the expansion of the Univer...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a sphere of radius R with charge density distributed as : ...
Text Solution
|
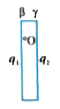
- Two fixed, identical conducting plates (a and (3), each of surface are...
Text Solution
|
- There is another useful system of units, besides the SI/mKs. A system,...
Text Solution
|
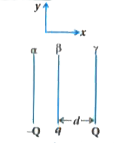
- Two charges -q each are fixed separated by distance 2d. A third charge...
Text Solution
|
- Total charge - Q is uniformly spread along length of a ring of radius ...
Text Solution
|