Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section D ( Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) )|93 VideosELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section D ( MCQs asked in Cometitive Exams )|39 VideosELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section C ( NCERT Exemplar Solution ) (Short ,Aswer Type Questions )|5 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise BOARD.S QUESTION PAPER MARCH - 2020 (PART - B) SECTION - C|5 VideosMAGNETISM AND MATTER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION D Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) (MCQs asked in Competitive Exams) MCQs asked in Board Exam and GUJCET|7 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE-Section C ( NCERT Exemplar Solution ) ( Long Answer Type Questions )
- Find the equation of the equipotential for an infinite cylinder of rad...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges of magnitude + q and - q are placed at (-(d)/(2),0,0...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel plate capacitor is filled by a dielectric whose relative pe...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor is made of two circular plates of radius R each, separated...
Text Solution
|
- In a quark model of elementary particles a neutron is made of one up q...
Text Solution
|
- Repeal above exercise for a proton which is made of two up and one dow...
Text Solution
|
- Two metal spheres, one of radius R and the other of radius 2R, both ha...
Text Solution
|
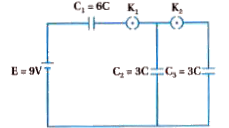
- In the circuit shown in figure, initially K(1) is closed and K(2) is ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate potential on the axis of a disc of radius R due to a charge ...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges q(1) and q(2) are placed at (0, 0, d) and (0, 0, - d) resp...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges - q each are separated by distanc · 2d. A third charge + q...
Text Solution
|
- In a Van-De Graaff type generator a spherical metal shell is to be a 1...
Text Solution
|