Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
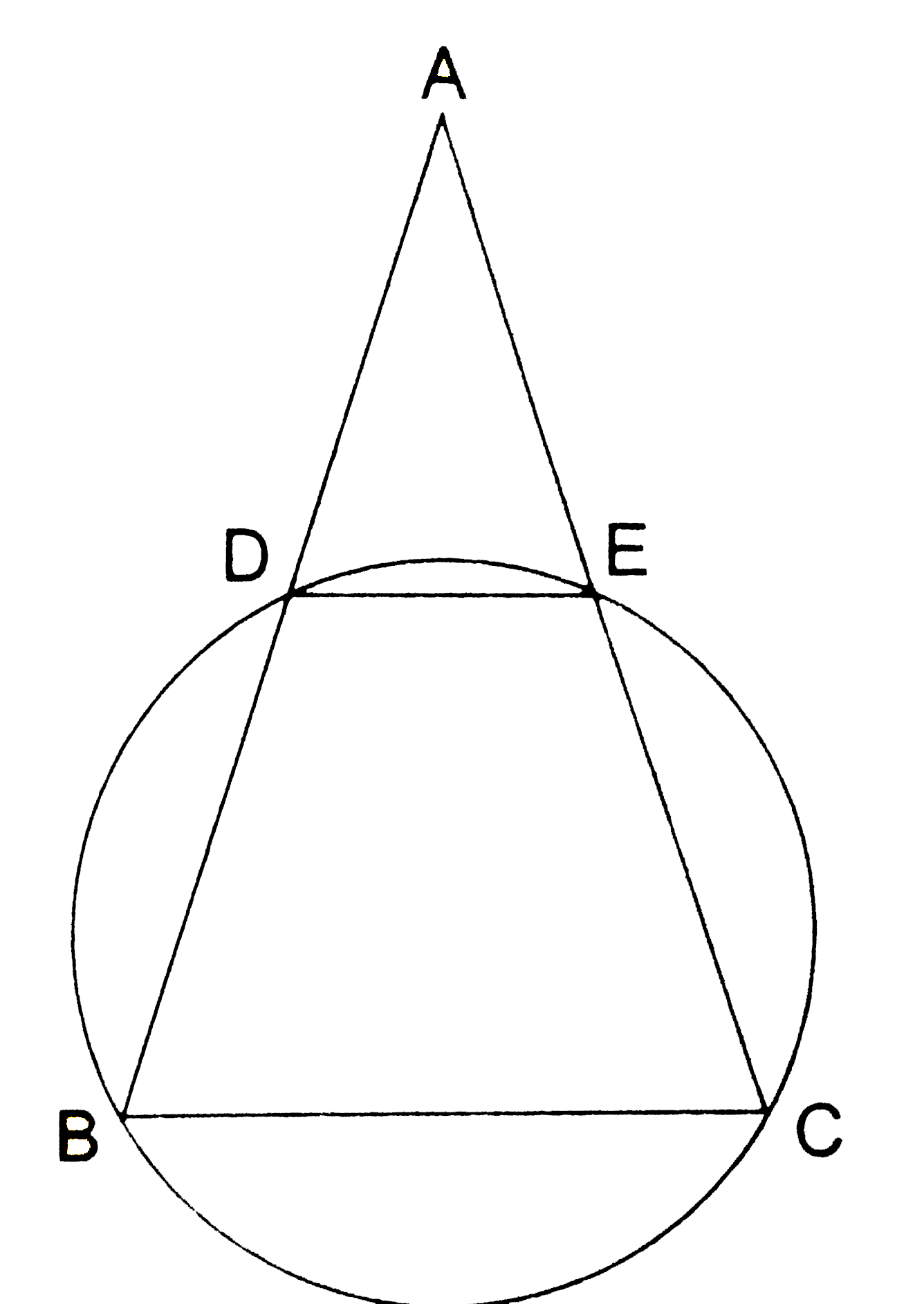
- In an isosceles triangle A B C with A B=A C , a circle passing t...
Text Solution
|
- Fill the blanks in the following so that each of the following stateme...
Text Solution
|
- D ,\ E ,\ F are the mid-point of the sides B C ,\ C A\ a n d\ A B re...
Text Solution
|
- D and E are points on equal sides A B and A C of an isosceles triangle...
Text Solution
|
- If D and E are points on sides A B and A C respectively of a trian...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure, A C=B C ,\ /D C A=/E C B\ a n d\ /D B C=E A Cdot Prove that...
Text Solution
|
- B D\ a n d\ C E are bisectors of /B\ a n d\ /C of an isosceles A B C ...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure, A B C is an isosceles triangle with A B=A C ,\ B D\ a n ...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure, A D=A E\ a n d\ D\ a n d\ E are points on B C such that B D...
Text Solution
|