Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
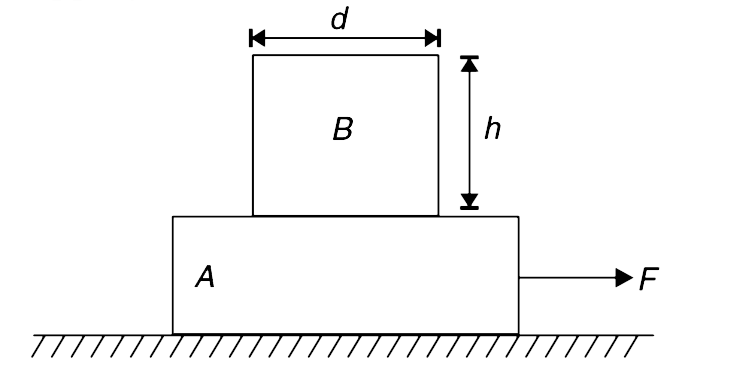
- Rectangular block B, having height h and width d has been placed on an...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses 4kg and 2kg are placed side on a smooth horizonta...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B each of mass m are placed on a smooth horizontal su...
Text Solution
|
- Rectangular block B, having height h and width d has been placed on an...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in the figure the coefficient of friction bet...
Text Solution
|
- On a smooth horizontal surface a block A of mass 10kg is kept. On this...
Text Solution
|
- A 2kg block is placed over a 4kg block and both are placed on a smooth...
Text Solution
|
- A 2kg block is placed over a 4kg block and both are placed on a smooth...
Text Solution
|
- A 2kg block is placed over a 4kg block and both are placed on a smooth...
Text Solution
|