Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MACHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-C|66 VideosMACHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-D|29 VideosMACHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-A TRY YOURSELF (VSQs)|40 VideosLAW OF MOTION
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise (QUESTION PAPER) SECTION-D|1 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise QUESTION PAPER (SECTION -C)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-MACHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS -SECTION-B
- What is the density of water at a depth where pressure is 80.0 atm, gi...
Text Solution
|
- Compute the fractional change in volume of a glass slab, when subjecte...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the volume contraction of a solid copper cube, 10 cm on an e...
Text Solution
|
- How much should the pressure on a litre of water be changed to compres...
Text Solution
|
- Anvils made of single crystals of diamond, with the shape as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length 1.05 m having negligible mass is supported at its ends...
Text Solution
|
- A mild steel wire of length 1.0 m and cross sectional area 0.50 xx 10 ...
Text Solution
|
- Two strips of metal are riveted together at their ends by four rivets,...
Text Solution
|
- The Marina trench is located in the Pacific Ocean, and at one place it...
Text Solution
|
- A steel wire of length 5 m and diameter 10^(-3) m is hanged vertically...
Text Solution
|
- A mass of 15 kg is tied at the end of a steel wire of the length lm. I...
Text Solution
|
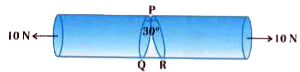
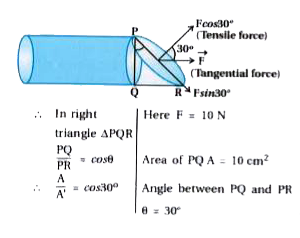
- As shown in figure 10 N force is applied at two ends of a rod. Calcula...
Text Solution
|
- Length and cross sectional area of a wire are 5 m and 2.5 mm^(2). Calc...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a composite rod of cross-sectional area 10^(-4) m^(2) mad...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of length L and cross section area A is kept on a horizontal su...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in figure, masses of 2 kg and 4kg are tied to two ends of a w...
Text Solution
|
- A steel wire of cross section 1 mm2 is heated at 60^(@) C and tied bet...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a wire of length 2L and crosssectional area A, stretched ...
Text Solution
|
- An object of mass 5 kg is suspended by a copper wire of length 2 m and...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for elastic potential energy per unit volume stor...
Text Solution
|