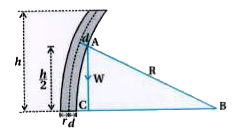
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MACHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-E|28 VideosMACHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-F|11 VideosMACHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-C|66 VideosLAW OF MOTION
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise (QUESTION PAPER) SECTION-D|1 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise QUESTION PAPER (SECTION -C)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-MACHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS -SECTION-D
- A wire is suspended from the ceiling and stretched under the action of...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length 1 and negligible mass is suspended at its two ends by ...
Text Solution
|
- For an ideal liquid
Text Solution
|
- A copper and a steel wire of the same diameter are connected end to en...
Text Solution
|
- The Young's modulus for steel is much more than that for rubber. For t...
Text Solution
|
- The Young's modulus for steel is much more than that for rubber. For t...
Text Solution
|
- Identical springs of steel and copper are equally stretched. On which ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the Young's modulus for a perfect rigid body?
Text Solution
|
- What is the bulk modulus of a perfectly rigid body?
Text Solution
|
- A wire of length L and radius r is clamped rigidly at one end. When th...
Text Solution
|
- A steel rod of length 1 m and area of cross section 1 cm^(2) is heated...
Text Solution
|
- To what depth must a rubber ball be taken in deep sea so that its volu...
Text Solution
|
- A truck is pulling a car out of a ditch by means of a steel cable that...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical solid balls, one of ivory and the other of wet-clay are ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a long steel bar under a tensile stress due to force F acting...
Text Solution
|
- (a) A steel wire of mass u per unit length with a circular cross secti...
Text Solution
|
- A steel uniform rod of length 2L cross sectional area A and mass Mis s...
Text Solution
|
- An equilateral triangle ABC is formed by two copper rods AB and BC and...
Text Solution
|
- In nature the failure of structural members usually result from large ...
Text Solution
|
- A stone is tied to an elastic string of negligible mass and spring con...
Text Solution
|