Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SOLUTIONS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - A QUESTIONS (SELF - PRACTICE QUESTIONS)|37 VideosSOLUTIONS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - A QUESTIONS (TRY YOURSELF)|29 VideosSOLUTIONS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - E MCQs asked in GUJCET/Board Exam|69 VideosSAMPLE QUESTION PAPER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise [PART-B] SECTION - C|2 VideosSURFACE CHEMISTRY
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - E (MCQs asked in GUJCET/Board Exams)|52 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-SOLUTIONS -SECTION - A QUESTIONS
- Derive an equation for solution which shows relation between total pre...
Text Solution
|
- Explain ''Solubility of gaseous solute and vapour pressure of liquid s...
Text Solution
|
- Explain vapour pressure of solutions of solids in liquids.
Text Solution
|
- Explain ideal solution.
Text Solution
|
- What are non ideal solutions ? Explain non ideal solutions with positi...
Text Solution
|
- What is azeotropes ? Explain their types.
Text Solution
|
- What are colligative properties ?
Text Solution
|
- Write Raoult's law for non - volatile solute and volatile solvent and ...
Text Solution
|
- What is elevation in boiling point ? Explain.
Text Solution
|
- What is molal elevation ? Explain.
Text Solution
|
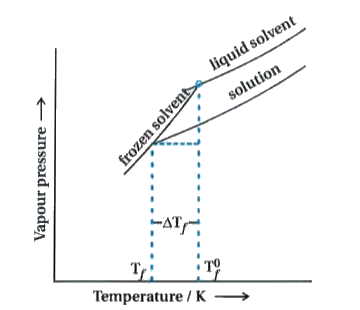
- What is depression of freezing point ? Explain.
Text Solution
|
- What is molal depression constant (K(f)) ? Derive equation relating K(...
Text Solution
|
- What is semi permeable membrane ? Give examples.
Text Solution
|
- Explain : What is osmosis ? Give example.
Text Solution
|
- What is osmotic pressure ? Explain and derive equation.
Text Solution
|
- Which method is most suitable to determine molecular mass of polymer ?
Text Solution
|
- Explain isotonic solutions.
Text Solution
|
- Explain reverse osmosis and purification of water.
Text Solution
|
- Explain abnormal molar masses. Also explain association and dissociati...
Text Solution
|
- Explain van't Hoff factor.
Text Solution
|