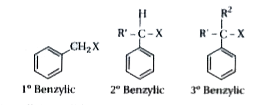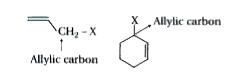Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - B INTEXT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS|20 VideosHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - C TEXTUAL EXERCISE|87 VideosHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - E Multiple Choice Questions|260 VideosGENERAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES OF ISOLATION OF ELEMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - E (MCQs ASKED IN GUJET/BOARD EXAMS)|46 VideosPOLYMERS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - E (MCQs asked in Board Exams)|51 Videos
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES-SECTION - A QUESTIONS
- State the uses of halogen containing organic compounds.
Text Solution
|
- Explain classification of haloalkanes and haloarenes on the basis of n...
Text Solution
|
- Explain classification of monohalogen compounds on the basis of sp^(3)...
Text Solution
|
- Write a note on the halogen compounds containing sp^(2)C-X bonds.
Text Solution
|
- Explain IUPAC nomenclature for halosubstituted hydrocarbons.
Text Solution
|
- Explain isomerism in Haloalkanes.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the nature of C - X bond in alkyl halides.
Text Solution
|
- Given preparation of alkyl halides from alcohols.
Text Solution
|
- Give preparation of haloalkanes from hydrocarbons.
Text Solution
|
- Explain preparation of alkyl halides by halogen exchange methods.
Text Solution
|
- Give preparation of aryl halides from aromatic hydrocarbons.
Text Solution
|
- Give preparation of haloarenes from amine compounds.
Text Solution
|
- Write a note on physical properties of haloalkanes and haloarenes.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following terms : Plane polarised light
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following terms : Optical activity
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following terms : Chirality
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following terms : Chiral centre (atom) and Achiral mo...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following terms : Enantiomers
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following terms : Diastereomers
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following terms : Meso compounds
Text Solution
|