Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - B INTEXT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS|20 VideosHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - C TEXTUAL EXERCISE|87 VideosHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - E Multiple Choice Questions|260 VideosGENERAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES OF ISOLATION OF ELEMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - E (MCQs ASKED IN GUJET/BOARD EXAMS)|46 VideosPOLYMERS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - E (MCQs asked in Board Exams)|51 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES-SECTION - A QUESTIONS
- Enlist the main points of difference between S(N)1 and S(N)2 reactions...
Text Solution
|
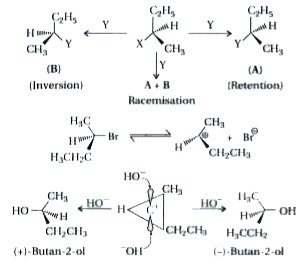
- What is retention and inversion of configuration ? Explain with suitab...
Text Solution
|
- Explain stereochemistry of S(N)1 reaction with suitable example.
Text Solution
|
- Explain stereochemistry of S(N)2 reaction with suitable example.
Text Solution
|
- Explain Elimination reactions of alkyl halides.
Text Solution
|
- Explain dehydrohalogenation (beta - elimination) of alkyl halides.
Text Solution
|
- Explain how sustitution and elimination reactions compete in the same ...
Text Solution
|
- Write a note on Grignard Reagent.
Text Solution
|
- Write a note on Wurtz Reaction.
Text Solution
|
- Explain why aryl halides are extermely less reactive towards nucleophi...
Text Solution
|
- Give the reaction of hydroxyl group with chlorobenzene.
Text Solution
|
- Explain why the electron withdrawing groups such as -NO(2) show its ef...
Text Solution
|
- Why aryl halides undergo electrophilic substitution reactions at o - a...
Text Solution
|
- Give following reaction of aryl halides : (i) Halogenation (ii...
Text Solution
|
- Give reactions of aryl halides with metals.
Text Solution
|
- State the various uses of : Dichloromethane (Methylene chloride)
Text Solution
|
- State the various uses of : Trichloromethone (Chloroform)
Text Solution
|
- State the various uses of : Tri - iodomethane (Iodoform)
Text Solution
|
- State the various uses of : Tetrachloromethane (Carbon tetrachlorid...
Text Solution
|
- State the various uses of : Freons
Text Solution
|