Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
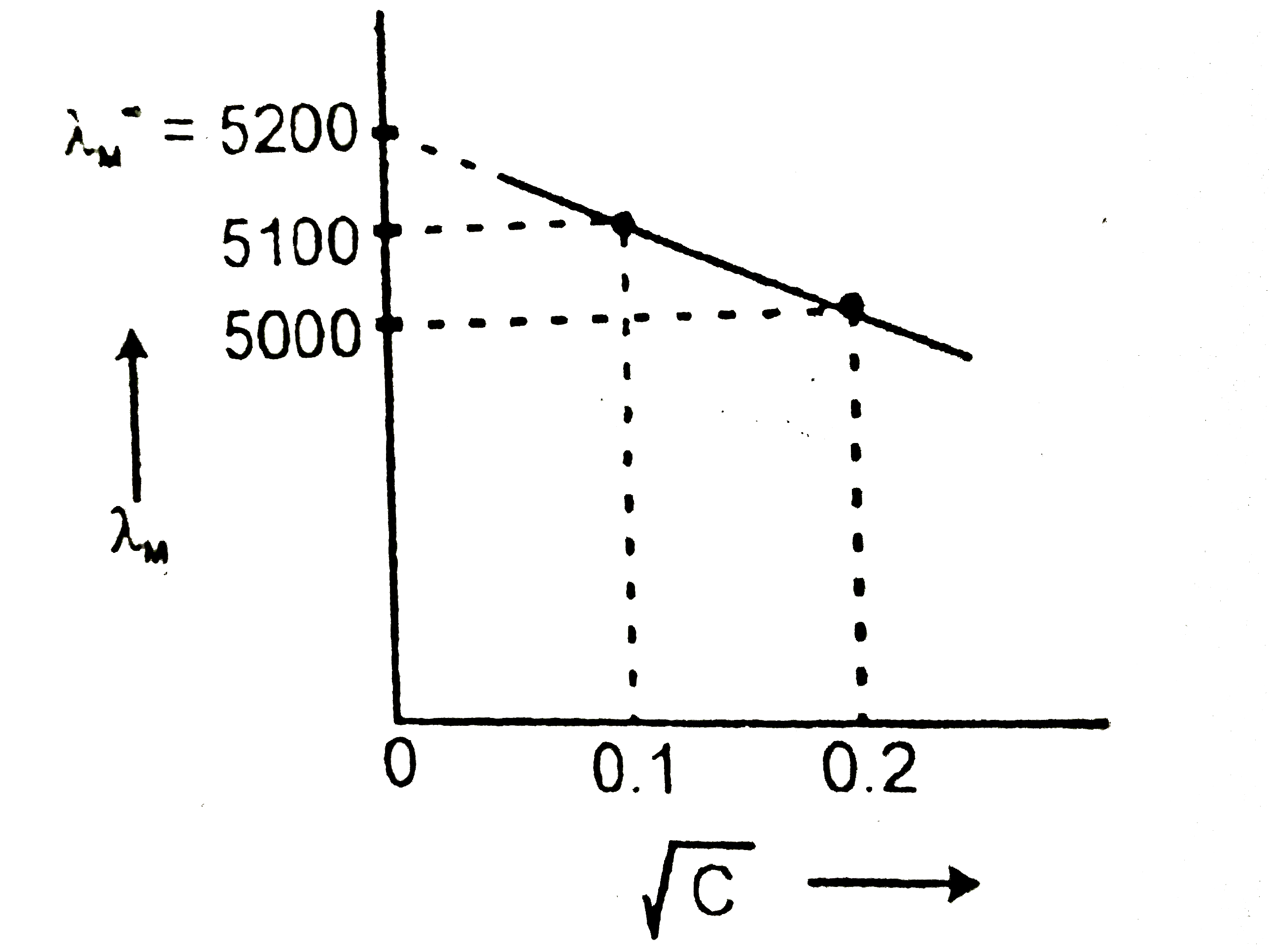
- At 0.04 M concentration the molar conductivity of a solution of a elec...
Text Solution
|
- For a dilute solution of a strong electrolyte, the variation of molar ...
Text Solution
|
- At 0.04 M concentration, the molar conductivity of solution of an elec...
Text Solution
|
- The molar conductivity of 0.05 M solution of weak acid is 16.6Omega^(-...
Text Solution
|
- Molar conductivity of a 1.5 m solustion of an electrolyte is found to ...
Text Solution
|
- At 0.04 M concentration the molar conductivity of a solution of a elec...
Text Solution
|
- The molar conductivity of a 1.5 M solution of an electrolyte is found ...
Text Solution
|
- प्रबल विद्युत-अपघट्य किसे कहते है? BaCl(2) के जलीय विलयन की अनंत तनुता...
Text Solution
|
- Molar conductivity of 0.1 (M) solution of a weak electrolyte is "0.009...
Text Solution
|