Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A wheel is rolling straight on ground without slipping. If the axis of...
Text Solution
|
- A hoop rolls on a horizontal ground without slipping with linear speed...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel rolls without slipping on a horizontal surface such that its v...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel is rolling straight on ground without slipping. If the axis of...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel of radius R rolls on the ground with a uniform velocity v. The...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel of radius R rolls without slipping on a horizontal ground. The...
Text Solution
|
- A bicycle wheel rolls without slipping on a horizonatal floor.W hich o...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel of radius R rolls on the ground with a uniform velocity v. The...
Text Solution
|
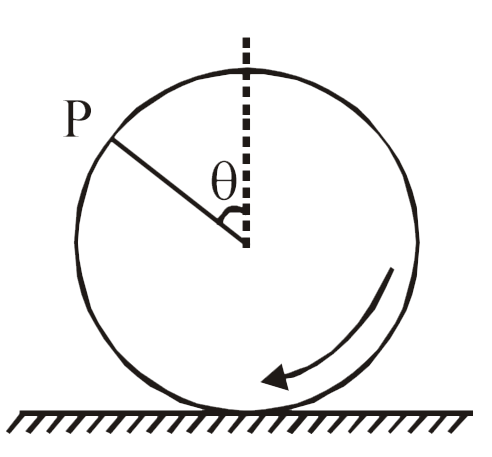
- A wheel of radius 'R' is placed on ground and its contact point 'P'. I...
Text Solution
|