Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
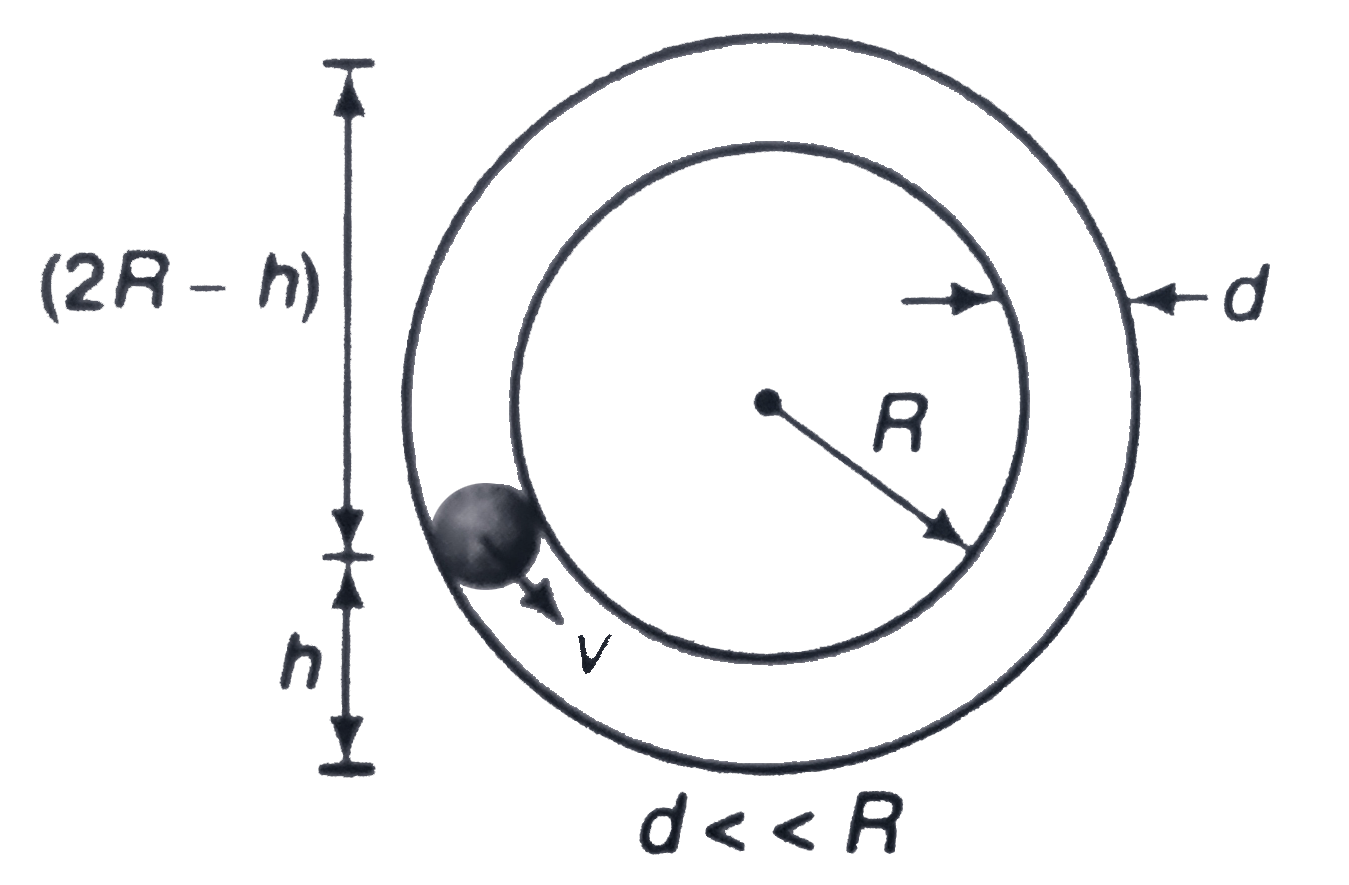
- With what minimum speed v must a small ball should be pushed inside a ...
Text Solution
|
- With what minimum speed v must a small ball should be pushed inside a ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m is moved with speed v0 at the highest point in a clos...
Text Solution
|
- There is a long vertical tube of radius r containing air at atmospheri...
Text Solution
|
- A capillary tube is made of glass of refractive index n' . The outer r...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball is pushed from a height h along a smooth hemispherical bo...
Text Solution
|
- A capillary tube of radius r is placed in a liquid I the angle of con...
Text Solution
|
- In a vertical smooth hollow thin tube, a block of same mass as that of...
Text Solution
|
- Water is flowing through a tube of radius r with a speed v. If this tu...
Text Solution
|