Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
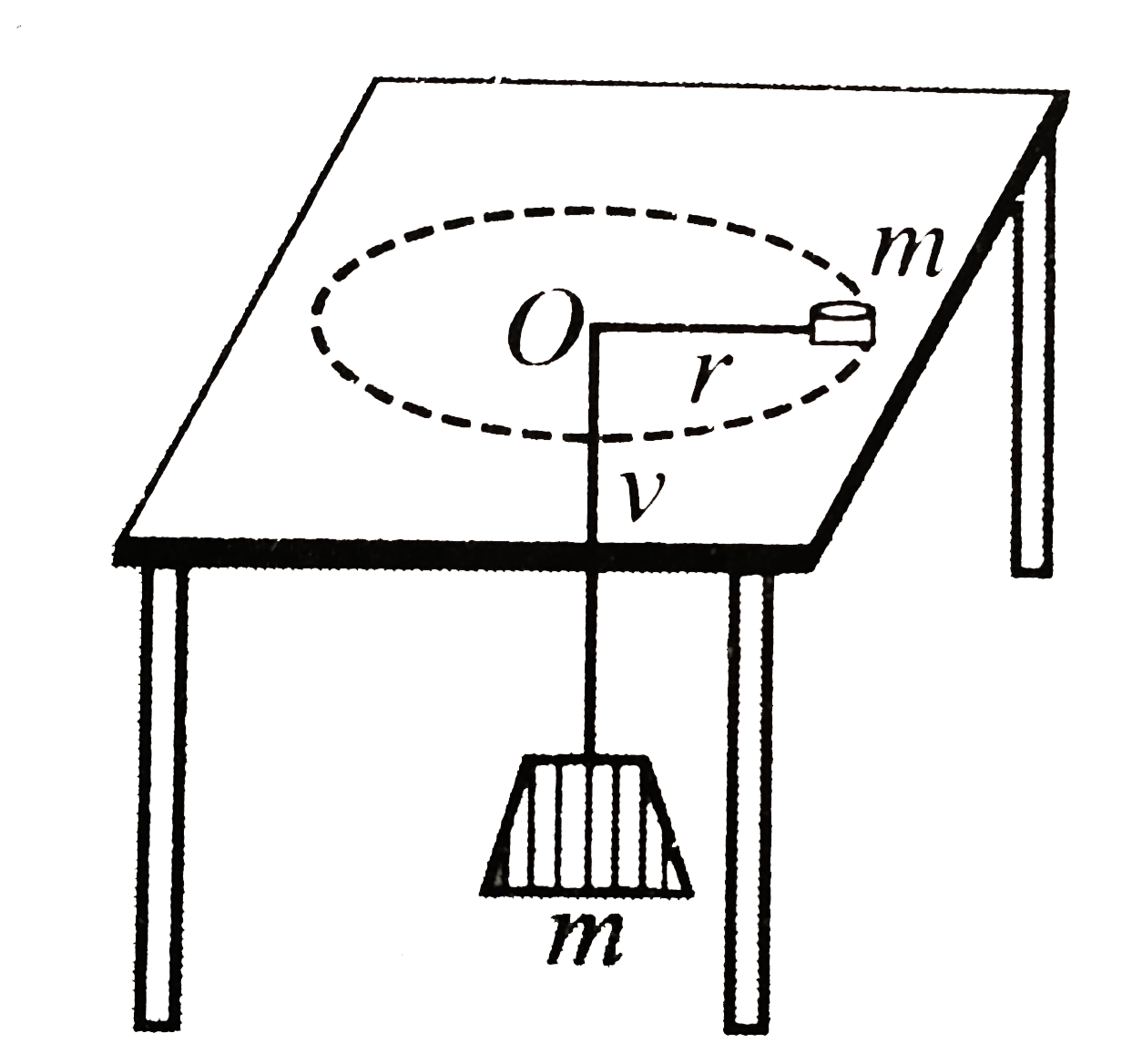
- A thread is passing through a hole at the centre of frictionless table...
Text Solution
|
- A thread is passing through a hole at the centre of frictionless table...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M is situation on a smooth horizontal frictionless tab...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m(1) rests on a horizontal table. A string tied to the...
Text Solution
|
- A block A of mass 7 kg is placed on a frictionless table. A thread tie...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m rotating freely in a horizontal circle of a radius 1m on a fr...
Text Solution
|
- द्रव्यमान 10 किग्रा का एक ब्लॉक एक क्षैतिज मेज पर रखा है जिससे एक डोरी...
Text Solution
|
- द्रव्यमान 3.0 किग्रा का एक पिण्ड एक घर्षण रहित क्षैतिज मेज पर रखा है ज...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of masses 1 kg 3 kg are tied at the two ends of a thread 60...
Text Solution
|