Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
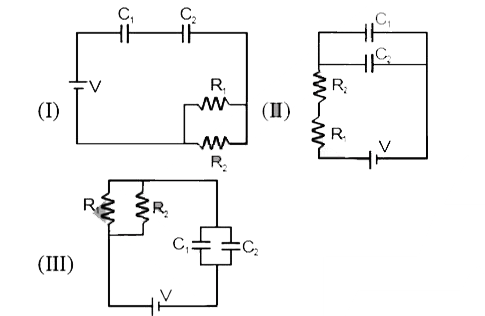
- Given : R1 =1ohm, R2 = 2ohm, C1 = 2 muF, C2 = 4muF The time consta...
Text Solution
|
- C1 and C2 are fixed circles of radii r1 and r2 touches each other exte...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a series of 'n' concentric circles C1, C2, C3, ....., Cn with...
Text Solution
|
- Find the charges on the three capacitors connected to a bettery as sho...
Text Solution
|
- Find the charges on the three capacitors connected to a bettery as sho...
Text Solution
|
- Find the time constant (in ) fo the given RC circuits in the given ord...
Text Solution
|
- Two Cars C1 and C2 are going round in concentric circles of radii R1 a...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the correct statement (s) related to the R1 R2 , C1 and C2 of...
Text Solution
|
- Given : R1 =1ohm, R2 = 2ohm, C1 = 2 muF, C2 = 4muF The time consta...
Text Solution
|