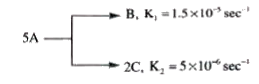A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL KINETICS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET-4 (MATCH THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS)|2 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET-4 (INTEGER ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS)|6 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET-4 (SINGLE OR MORE THAN ONE OPTION QUESTIONS)|16 VideosCHEMICAL KINETCS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise EXERCISE - 3.2|45 VideosCHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Additional Practice Exercise|54 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-CHEMICAL KINETICS-PRACTICE SHEET-4 (LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE QUESTIONS)
- A follows parallel path first order reaction to give B and C as given ...
Text Solution
|
- A follows parallel path first order reaction to give B and C as given ...
Text Solution
|
- A follows parallel path first order reaction to give B and C as given ...
Text Solution
|
- Elementary unimolecular reaction have first order rate laws, elementar...
Text Solution
|
- Elementary unimolecular reaction have first order rate laws, elementar...
Text Solution
|
- Elementary unimolecular reaction have first order rate laws, elementar...
Text Solution
|