Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HEREDITY AND EVOLUTION
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise TOPIC - 1 (HEREDITY AND MENDEL.S CONTRIBUTION)(LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS)|6 VideosHEREDITY AND EVOLUTION
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise TOPIC - 2 (ORIGIN OF LIFE AND EVOLUTION)(MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION)|1 VideosHEREDITY AND EVOLUTION
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise TOPIC - 1 (HEREDITY AND MENDEL.S CONTRIBUTION)(SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS - I)|10 VideosCONTROL AND CO-ORDINATION
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT CORNER (Textbook Exercises)|12 VideosHOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE?
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT CORNER (TEXTBOOK EXERCISES)|11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OSWAAL PUBLICATION-HEREDITY AND EVOLUTION-TOPIC - 1 (HEREDITY AND MENDEL.S CONTRIBUTION)(SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS - II)
- In human beings, the statistical probability of getting either a male ...
Text Solution
|
- How do Mendel's experiments show that traits may be dominant or recess...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Name the unit of inheritance. What is its function? (ii) How are...
Text Solution
|
- Show inheritance of two characters over two generations by making a cr...
Text Solution
|
- In a cross between plants with purple flowers and plants with white fl...
Text Solution
|
- In one of his experiments with pea plants Mendel observed that when a ...
Text Solution
|
- List three distinguishing features, in tabular form, between acquired ...
Text Solution
|
- In a monohybrid cross between tall pea plants (TT) and short pea plant...
Text Solution
|
- 'Different species use different strategies to determine sex of a newb...
Text Solution
|
- What will happen if both the characters present in F(1) generation pas...
Text Solution
|
- A pea plant with blue colour flower denoted by BB is cross-bred with a...
Text Solution
|
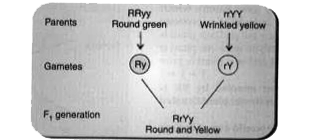
- A cross was made between pure breeding pea plant one with round and g...
Text Solution
|
- In one of his experiments with pea plants Mendel observed that when a ...
Text Solution
|
- A cross was carricd out between a pure bred tall pea plant and a pure ...
Text Solution
|
- A blue colour flower plant denoted by BB is crossbred with a white col...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Differentiate between dominant and recessive traits. (ii) 'Gene ...
Text Solution
|
- The genotype of green-stemmed tomato plants is denoted by GG and that ...
Text Solution
|
- With the help of a cross done with garden pea plants, trace the work d...
Text Solution
|
- In Mendel's monohybrid cross between tall and short pea plants, all of...
Text Solution
|
- Explain with the help of a figure that father is responsible for the s...
Text Solution
|