Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
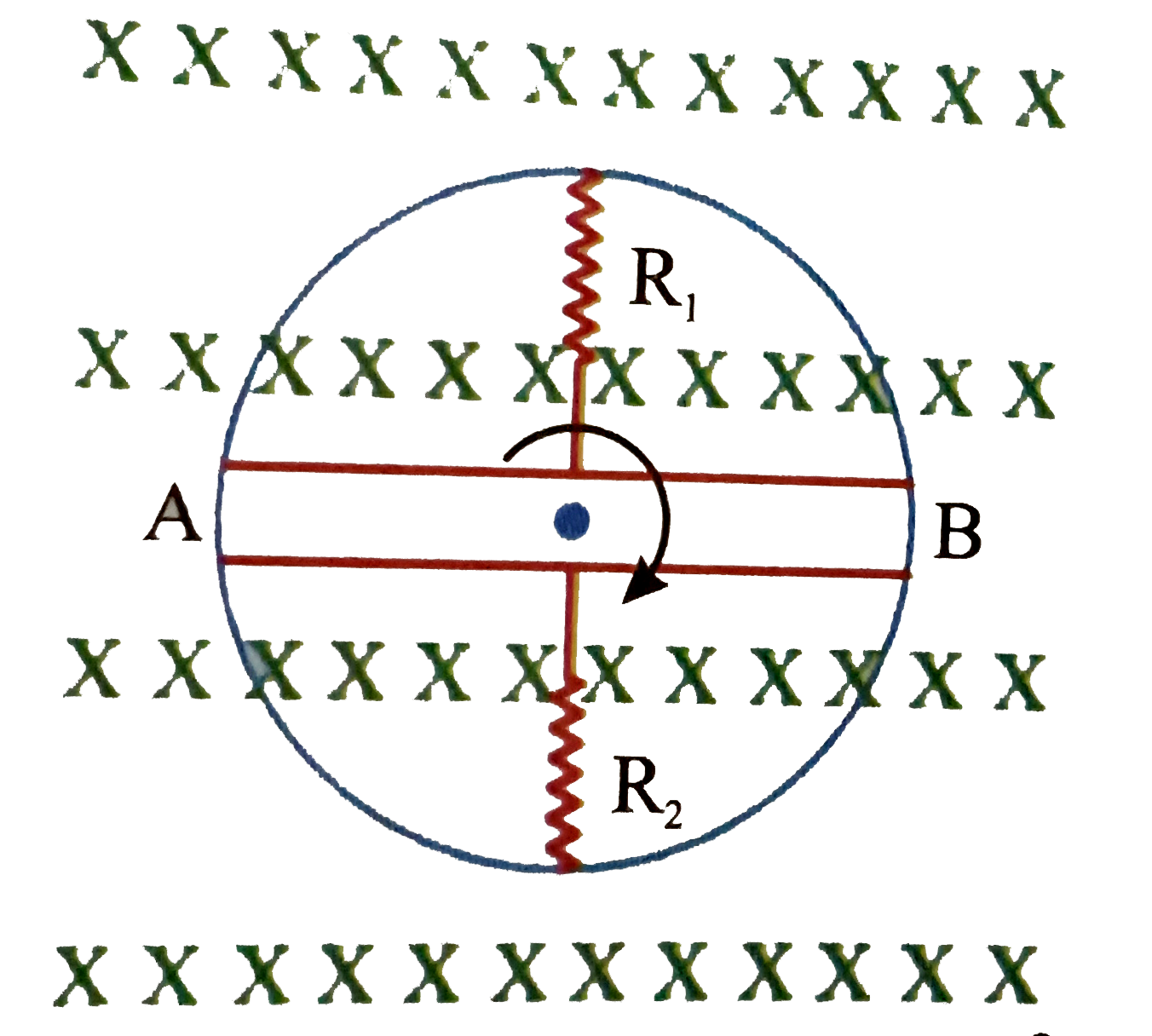
- AB is a resistanceless conducting rod which forms a diameter of a cond...
Text Solution
|
- Two long parallel conducting rails are placed in a uniform magnetic fi...
Text Solution
|
- AB is a resistanceless conducting rod which forms a diameter of a cond...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mas m is moving with constant velocity v(0) in a perp...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting open pipe has shape of a half cylinder of length L. Its s...
Text Solution
|
- Two resistors of resistance R(1) and R(2) having R(1) gt R(2) are conn...
Text Solution
|
- Two resistors of resistances R(1)=100 pm 3 ohm and R(2)=200 pm 4 ohm a...
Text Solution
|
- If R(1) and R(2) are the resistance of two solution of equal volume, ...
Text Solution
|
- Four resistors R(1) , R(2) , R(3) and R(4) are connected in parallel ....
Text Solution
|