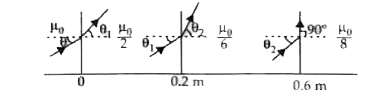
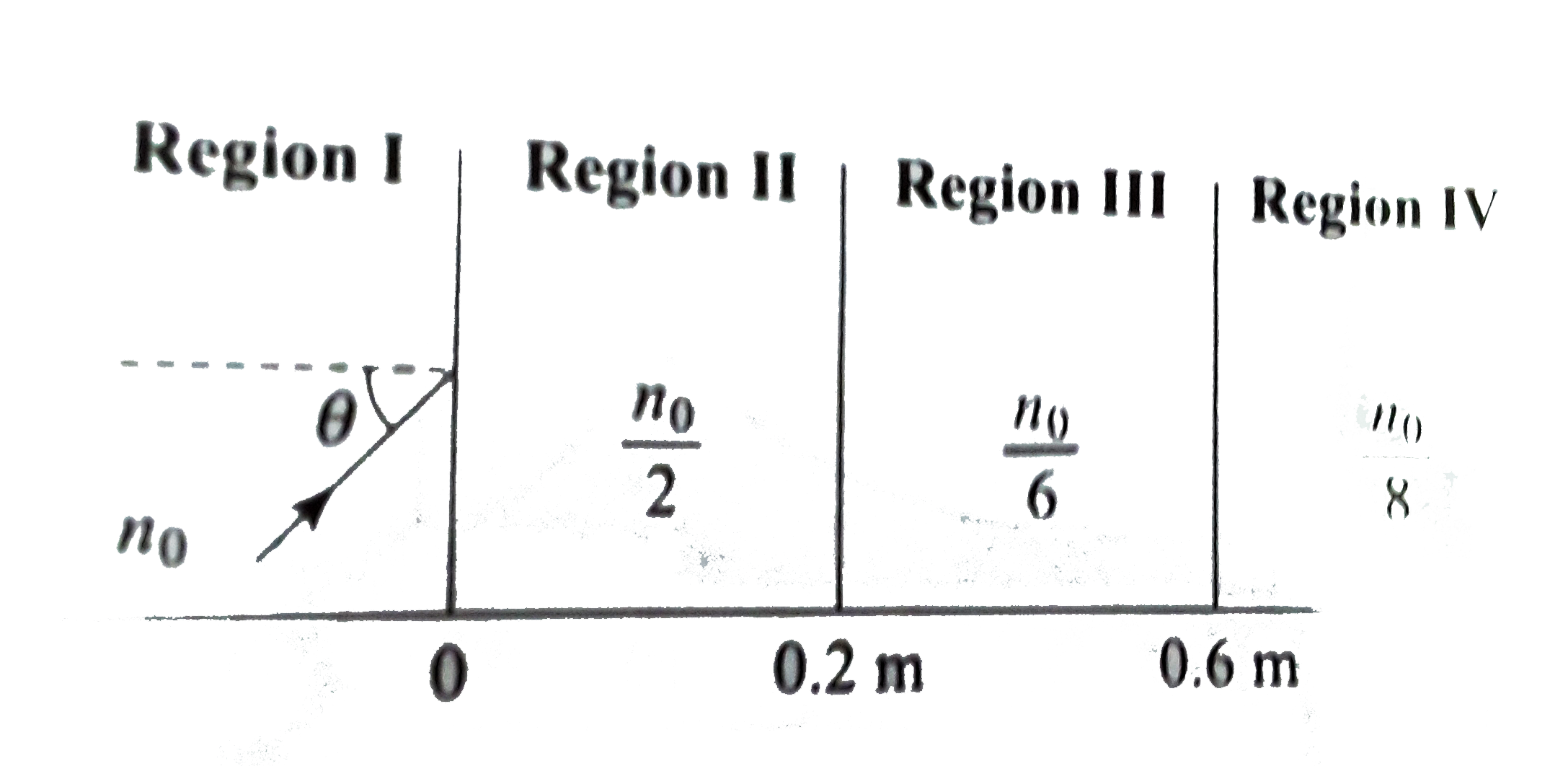A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MTG GUIDE-OPTICS-Topicwise Practice Questions
- A ray of light is incident at the glass-water interface at an angle i ...
Text Solution
|
- A,B, and C are the parallel sided transparent media of refractive indi...
Text Solution
|
- A light beam is traveling from Region I to region IV (refer figure). T...
Text Solution
|
- Refraction of light from air to glas and from air to water are shown i...
Text Solution
|
- The refractive index of water, glass and diamond are 1.33, 1.50, 2.40 ...
Text Solution
|
- A vesse of depth x is half filled with oil of refractive index mu(1) a...
Text Solution
|
- Sun is visible a little before the actual sunrise and until a little a...
Text Solution
|
- When a light ray centers a refracing medium, it is found that the magn...
Text Solution
|
- A metal coin at the bottom of a beaker filled with a liquid of refrac...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is used in optical fibres?
Text Solution
|
- If the critical angle for total internal reflection from a medium to v...
Text Solution
|
- Critical angle of glass is theta(1) and that of water is theta(2). The...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray is incident normally on the face AB of a right-angled pris...
Text Solution
|
- A fish looking from within water sees the outside world through a circ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident at an angle alpha on the boundary separatin...
Text Solution
|
- Critical angle for light going from medium (i) to (ii) is theta . The ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travelling in water is incident on its surface open to ...
Text Solution
|
- A glass prism of refractive index 1.5 is immersed in water (refractive...
Text Solution
|
- Light travels in two media A and B with speeds 1.8 × 10^(8) m s^(–1) a...
Text Solution
|
- A bulb is placed at a depth of 2sqrt7cm in water and a floating opaque...
Text Solution
|