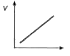
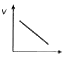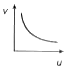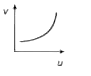A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MCGROW HILL PUBLICATION-REFLECTION OF LIGHT -HIGHER ORDER THINKING QUESTIONS
- If velocity of radio waves is 3 xx 10^8 m/s, the frequency correspondi...
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror of focal length f (in air) is immersed in water (mu=4...
Text Solution
|
- Signal from a remote control to the device operated by it travels with...
Text Solution
|
- In case of a concave mirror, when we move the object from infinity to ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident on a convex mirror at angle of incidence of...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light strikes a silvered surface inclined to another one at a...
Text Solution
|
- The focal length (f) of a spherical mirror of radius of curvature R is
Text Solution
|
- A beam of light incident on a plane mirror forms a real image on refle...
Text Solution
|
- A mirror produces magnified erect image of an object. The nature of th...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray is incident normally on a plane mirror. The angle of refle...
Text Solution
|