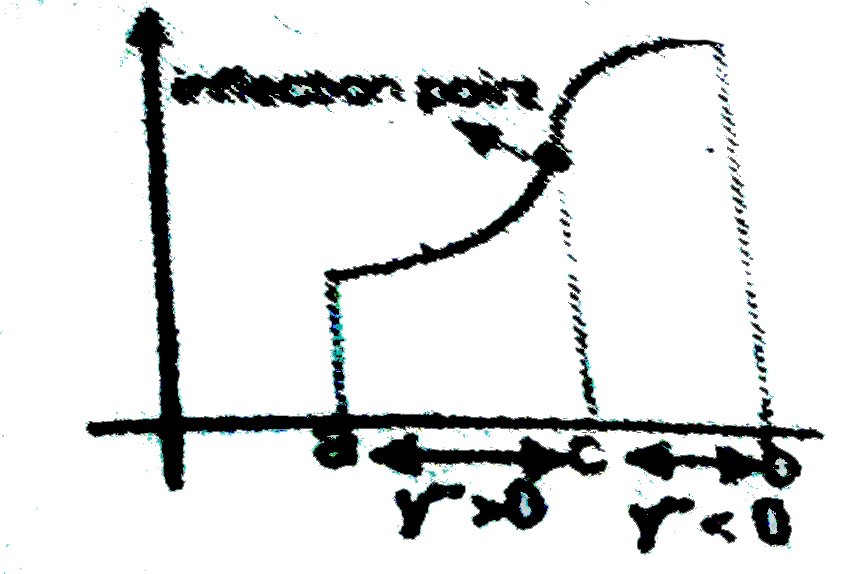Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Concavity and convexity : if f''(x) gt 0 AA x in (a,b) then the c...
Text Solution
|
- Concavity and convexity : if f''(x) gt 0 AA x in (a,b) then the c...
Text Solution
|
- Concavity and convexity : if f''(x) gt 0 AA x in (a,b) then the c...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the point of symmetry of a regular hexagon. <img src="htt...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following Column A to Column B
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, PQRS is a parallelogram. A and B are the mid-poin...
Text Solution
|
- At x=0, value of (dy)/(dx) is : ltimg src="https://d10lpgp6xz60nq.clou...
Text Solution
|
- If y-x=180^(@) then find the values of x and y. ltimg src="https://d10...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x)=ax+b, a lt 0, then f^(-1)(x)=f(x)AA x if and only if
Text Solution
|