Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A source and detector both start moving simultaneously fro the positio...
Text Solution
|
- A source and a detector moveaway fro each other, each with a speed of ...
Text Solution
|
- A small source of sound oscillates in simple harmonic motion with an a...
Text Solution
|
- Source and observer start moving simulatneously along x and y-axis res...
Text Solution
|
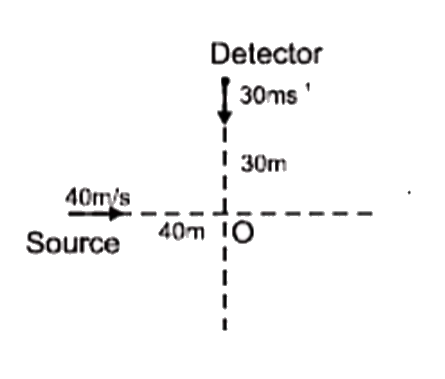
- A source of sound and detector are arranged as shown in Fig. The detec...
Text Solution
|
- A source of sound and detector are arranged as shown in Fig. The detec...
Text Solution
|
- A source and detector both start moving simultaneously from the positi...
Text Solution
|
- Source and observer both start moving simultaneously from origin one a...
Text Solution
|
- A source and a detector move away from each other, each with a speed o...
Text Solution
|