Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
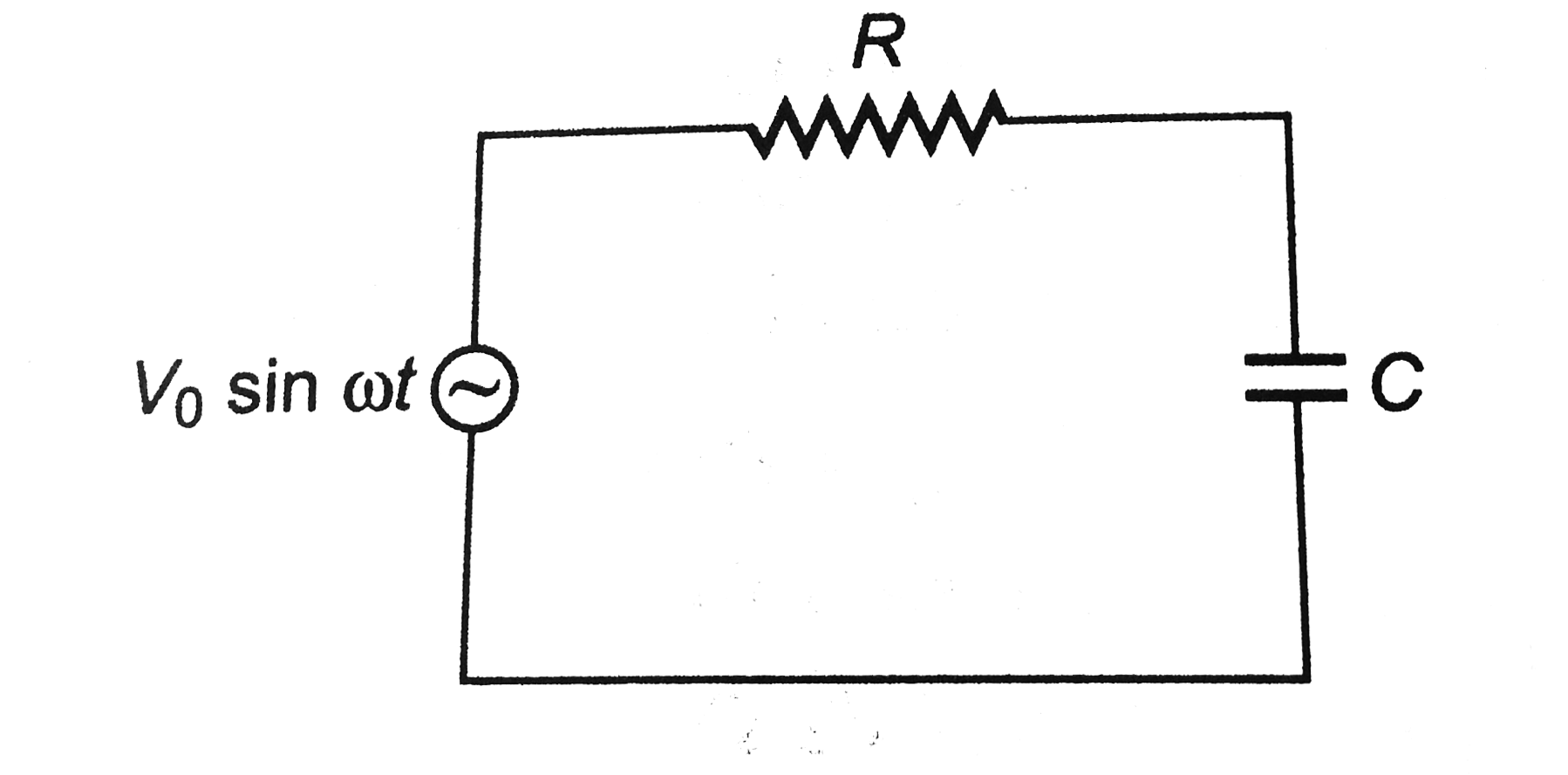
- An AC voltage source V=V0siomegatis connected across resistance R and ...
Text Solution
|
- An inductor (L = 200 mH) is connected to an AC source of peak emf 210 ...
Text Solution
|
- A 50 Hz AC source of 20 V is connected across R and C as shown in figu...
Text Solution
|
- Consider in L-C-R circuit as shown in figureure with an AC source of p...
Text Solution
|
- An AC voltage source V=V0siomegat is connected across resistance R and...
Text Solution
|
- An AV voltage source is applied across an R-C circuit. Angular frequen...
Text Solution
|
- An LCR circuit (R=40Omega,L=100mH,C=0.242muF) is connected with an ac ...
Text Solution
|
- एक श्रेणी LCR परिपथ में प्रत्यावर्ती वोल्टता 230 V का स्रोत जुड़ा है। य...
Text Solution
|
- Resistor of resistance R and capacitor of capacitance C are connected ...
Text Solution
|
 .
.