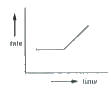
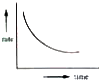
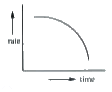
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
SURFACE CHEMISTRY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET - 3 (MATCH THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS)|2 VideosSURFACE CHEMISTRY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET - 3 (INTEGER ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS)|6 VideosSURFACE CHEMISTRY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET - 3 (SINGE OR MORE THAN ONE OPTION QUESTIONS)|16 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET (ADVANCED) (INTEGER TYPE QUESTION)|2 VideosVA GROUP ELEMENTS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE EXERCISE|51 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-SURFACE CHEMISTRY-PRACTICE SHEET - 3 (LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE QUESTIONS)
- A catalyst alters the rate of a reaction by leading of increasing the ...
Text Solution
|
- A catalyst alters the rate of a reaction by leading of increasing the ...
Text Solution
|
- A catalyst alters the rate of a reaction by leading of increasing the ...
Text Solution
|
- Micelles are formed from concentrated soap solutions above critical mi...
Text Solution
|
- Micelles are formed from concentrated soap solutions above critical mi...
Text Solution
|
- Micelles are formed from concentrated soap solutions above critical mi...
Text Solution
|